This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New research shows illusions are in the eye, not the mind's neurons
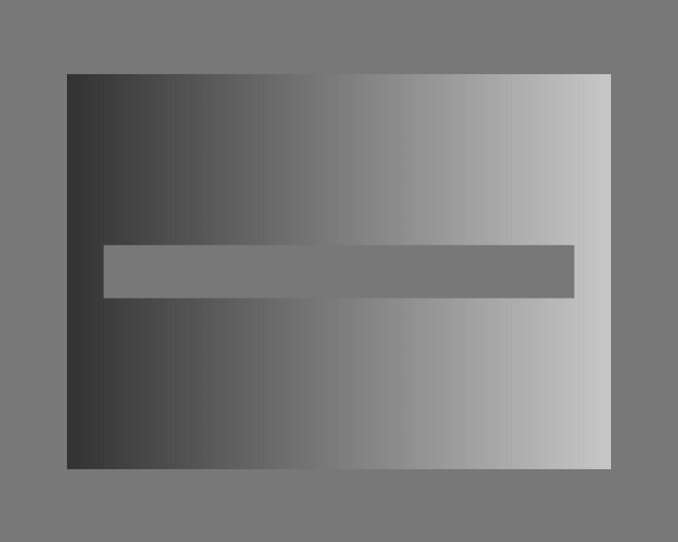

Numerous visual illusions are caused by limits in the way our eyes and visual neurons work—rather than more complex psychological processes, new research shows.
Researchers examined illusions in which an object's surroundings affect the way we see its color or pattern. The paper, published in the journal PLOS Computational Biology, is titled "A model of color appearance based on efficient coding of natural images."
Scientists and philosophers have long debated whether these illusions are caused by neural processing in the eye and low-level visual centers in the brain, or involve higher-level mental processes such as context and prior knowledge.
In the new study Dr. Jolyon Troscianko, from the University of Exeter, co-developed a model that suggests simple limits to neural responses—not deeper psychological processes—explain these illusions.
"Our eyes send messages to the brain by making neurons fire faster or slower," said Dr. Troscianko, from the Center for Ecology and Conservation on Exeter's Penryn Campus in Cornwall. "However, there's a limit to how quickly they can fire, and previous research hasn't considered how the limit might affect the ways we see color."
The model combines this "limited bandwidth" with information on how humans perceive patterns at different scales, together with an assumption that our vision performs best when we are looking at natural scenes.
-
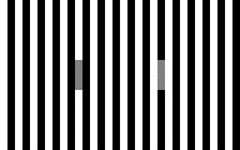
The two gray bars in the middle of this figure are the same gray, but the one on the left (surrounded by more black bars) appears darker. This is the opposite of the simultaneous contrast example above, because darker surrounds now make the target look darker. Credit: Jolyon Troscianko -
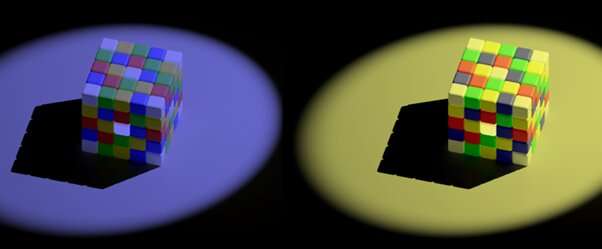
Both cubes have what appear to be yellow and blue tiles on their top surfaces. However, the ones that look yellow on the left are in fact a gray color that is identical to the blue tiles on the right. Our model can help explain how objects appear to be the same color even when the light changes, and why in illusions such gray looks colorful. Credit: Jolyon Troscianko
The model was developed by researchers from the Universities of Exeter and Sussex to predict how animals see color, but it was also found to correctly predict many visual illusions seen by humans.
"This throws into the air a lot of long-held assumptions about how visual illusions work," Dr. Troscianko said.
He said the findings also shed light on the popularity of high-definition televisions.
"Modern high dynamic range televisions create bright white regions that are over 10,000 times brighter than their darkest black, approaching the contrast levels of natural scenes," Dr. Troscianko added.
"How our eyes and brains can handle this contrast is a puzzle because tests show that the highest contrasts we humans can see at a single spatial scale is around 200:1.
"Even more confusingly, the neurons connecting our eyes to our brains can only handle contrasts of about 10:1.
"Our model shows how neurons with such limited contrast bandwidth can combine their signals to allow us to see these enormous contrasts, but the information is 'compressed'—resulting in visual illusions.
"The model shows how our neurons are precisely evolved to use of every bit of capacity.
"For example, some neurons are sensitive to very tiny differences in gray levels at medium-sized scales, but are easily overwhelmed by high contrasts.
"Meanwhile, neurons coding for contrasts at larger or smaller scales are much less sensitive, but can work over a much wider range of contrasts, giving deep black-and-white differences.
"Ultimately this shows how a system with a severely limited neural bandwidth and sensitivity can perceive contrasts larger than 10,000:1."
More information: A model of colour appearance based on efficient coding of natural images, PLoS Computational Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011117