This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Researchers discover potential new prescription strategy for ischemic stroke
A study conducted by scientists at LSU Health New Orleans' Neuroscience Center of Excellence reports that the additive neuroprotection of a combination of two omega-3 fatty acid-derived signaling molecules is more effective in protecting brain cells and increasing recovery from stroke in an experimental model than a single drug. Results were published online in Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology.
"We discovered a compelling effective combinatorial therapy in experimental stroke," notes Nicolas Bazan, MD, Ph.D., Director of the LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center and senior author of the study.
"Despite increasing knowledge of the physiologic, mechanistic, and imaging characterizations of stroke, no effective neuroprotective therapy has been found to date. Most current work uses different approaches with a 'single' bullet therapy. Since stroke is so complex and due to multiple damaging factors, we extensively explored a multidisciplinary approach, a combinatorial therapy, that yielded promising beneficial results."
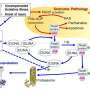
The research team examined the bioactivity of Neuroprotectin D1 (NPD1—discovered by the Bazan lab in 2003) combined with Resolvin D1 (RvD1) in experimental stroke. These two naturally occurring neuroprotective molecules in the brain derived from docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) called docosanoids have been shown to limit excessive inflammatory responses, regulate metabolism and immune cell functions, decrease the production of proinflammatory factors, and promote tissue repair and stability.
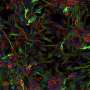
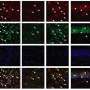
Under Dr. Bazan's guidance, LSU Health New Orleans graduate student and first author Madigan Reid designed and performed gene expression studies that showed the combination treatment elicited the selective expression of genes contributing to cell survival.
The scientists found that the combination therapy boosted the uptake of an anti-inflammatory stroke-associated gene by 123-fold, a gene that regulates new brain cell and blood vessel growth by 100-fold, and two markers of the stability of the brain cells that regulate brain development, maintenance of neuronal networks and injury repair by ten- and fivefold, respectively.
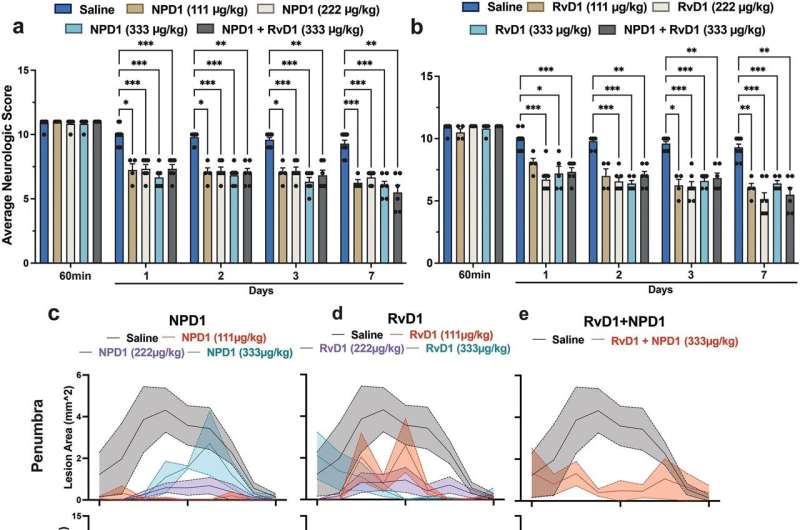
"We show that NPD1 + RvD1 remarkably improves neurological function and reduces lesion volume in acute ischemic stroke when administered promptly in moderate doses," adds Ludmila Belayev, MD, Professor of Neurosurgery, Neurology and Neuroscience at LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center.
"We also demonstrated a broad therapeutic window of neuroprotection with moderate doses of NPD1 + RvD1, such that treatment initiated even 6 hours after stroke onset is highly effective. This combinatorial therapy may promise future therapeutic development against ischemic stroke."
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, each year in the United States, there are more than 800,000 strokes. Stroke is a leading cause of death in the country and a leading cause of serious long-term disability. Stroke is a medical emergency. Every minute counts because the longer blood flow is cut off to the brain, the greater the damage. Immediate treatment can save people's lives and enhance their chances for successful recovery.
"The biological activity of NPD1 plus RvD1 is due to specific activation and modulation of signaling pathways associated with the immune system, inflammation, cell survival, and cell-cell interactions," concludes Dr. Bazan. "These findings provide a major conceptual advance of broad therapeutic relevance for cell survival, brain function and, particularly, stroke and neurodegenerative diseases."
More information: Madigan M. Reid et al, NPD1 Plus RvD1 Mediated Ischemic Stroke Penumbra Protection Increases Expression of Pro-homeostatic Microglial and Astrocyte Genes, Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s10571-023-01363-3