This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
A pragmatic approach for the detection of post-ablation atrial fibrillation recurrence
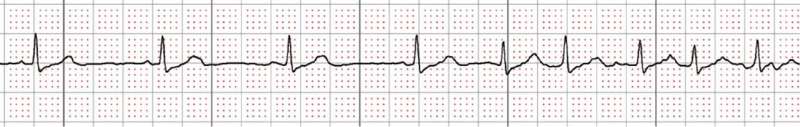
Symptom-driven electrocardiogram (ECG) recording plays a significant role in the detection of post-ablation atrial fibrillation recurrence (AFR). However, making timely medical contact whenever symptoms occur may not be practical. The authors of an article published in Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications deployed a deep learning (DL)-based handheld device to facilitate symptom-driven monitoring.
A cohort of patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) was trained to use a DL-based handheld device to record ECG signals whenever symptoms presented after the ablation. Additionally, 24-hour Holter monitoring and 12-lead ECG were scheduled at three, six, nine, and 12 months post-ablation. The detection of AFR by the different modalities was explored.
A total of 22 of 67 patients experienced AFR. The handheld device and 24-hour Holter monitor detected 19 and eight AFR events, respectively, five of which were identified by both modalities.
A larger portion of ECG tracings was recorded for patients with than without AFR [362(330) vs. 132(133), P=0.01)], and substantial numbers of AFR events were recorded from 18:00 to 24:00. Compared to Holter, more AFR events were detected by the handheld device in earlier stages (HR=1.6, 95% CI 1.2–2.2, P<0.01).
The DL-based handheld device-enabled symptom-driven recording, compared with the conventional monitoring strategy, improved AFR detection and enabled more timely identification of symptomatic episodes.
More information: Laite Chen et al, Deep Learning-based Handheld Device-Enabled Symptom-driven Recording: A Pragmatic Approach for the Detection of Post-ablation Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence, Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications (2023). DOI: 10.15212/CVIA.2023.0048