This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New blood test gives high accuracy screen for Alzheimer's disease
A new blood test called p-tau217 shows promise as an Alzheimer's disease biomarker, and when used in a two-step workflow very high accuracy to either identify or exclude brain amyloidosis, the most important and earliest pathology. That is an innovation now presented by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, together with colleagues at University of Lund and in Montreal, Canada.
In recent years, a lot of effort has been put on developing biomarkers in blood that could potentially help to identify Alzheimer's disease (AD). Tau protein, in particular its phosphorylated variant (p-tau)—and one of the main proteins involved in AD pathology—has been the focus of extensive research and developments the last years.
The new blood-based p-tau biomarkers, especially a variant called p-tau217, have shown great promise as clinically useful tools to screen patients with memory problems or other early cognitive symptoms suggestive of early Alzheimer's disease.
However, even if promising, a concern has been that classifying early patients into either having "AD or not AD" will still result in a rather high percentage of false positives (individuals with a positive test result who do not have AD) and false negatives (individuals with a negative test result who prove to have AD based on other examinations such as amyloid PET scans).
Considering not only ethical and psychological concerns induced by possible misdiagnosis, but also high costs and potential medical risks of initiating treatments on people not having the target disease), the scientists at the University of Gothenburg and their colleagues developed a novel strategy for the clinical implementation of blood biomarkers.
Two-step workflow
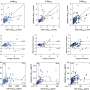
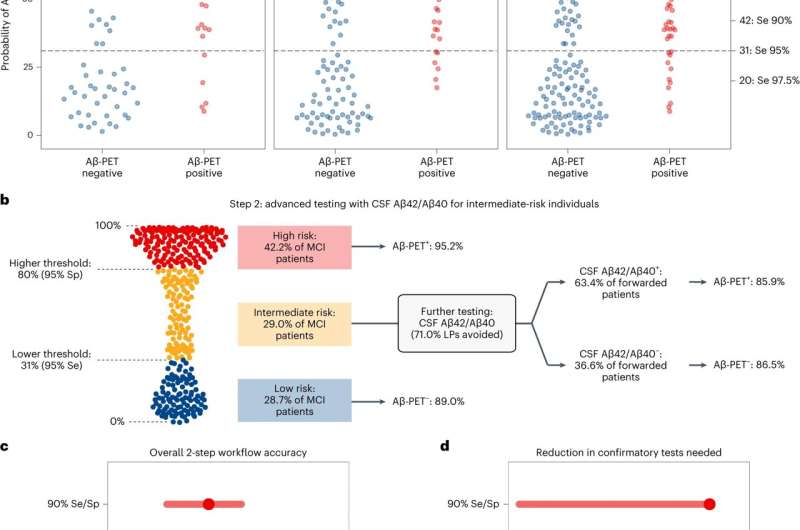
The two-step model is built on a first step with a diagnostic model (based on plasma p-tau217 together with age and APOE e4) to stratify patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) for risk of amyloid PET positivity. Step 2 is based on confirmatory testing with CSF Ab42/40 ratio (or amyloid EPT) only in those with uncertain outcomes in step 1.
The workflow was evaluated in 348 MCI participants from the Swedish BioFINDER studies (Lund University) and validated in the independent TRIAD cohort (McGill University, Montreal, Canada) also using an independent method for analysis of plasma p-tau217.
Very high accuracy
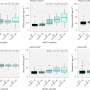
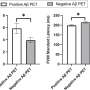
The model was evaluated at three different thresholding strategies were explored to classify participants into groups with low, intermediate and high risk for being "Aβ positive" (having AD-type pathology). At the stringent lower probability thresholds with 97.5% sensitivity (to avoid missing detection of patients who are Aβ positive), as little as 6.6% false negatives was found, while the stringent 97.5% specificity (to avoid classifying patients who are Aβ negative as 'high risk') gave only 2.3% false positives.
At the stringent sensitivity/specificity thresholds, 41% of patients fell into the intermediate risk group (compared to 29% of patients for the 95% thresholds). Further evaluations of this group with CSF Aβ42/40 showed very good agreement (86%) with amyloid PET results. Results were verified in the independent McGill cohort of patients.
A clinically useful strategy for p-tau217 blood test for AD screening
The study presents a blood plasma p-tau217-based two-step model for risk stratification of patients with MCI into high, low- and intermediate-risk of having brain amyloidosis and early AD pathology. The blood test applied in step 1 shows very high accuracy to identify high-risk patients, who depending on the clinical situation can either be given a diagnosis and be initiated on symptomatic treatments, or in the future be referred to the specialist clinic for possible initiation disease-modifying treatment.
In the low-risk group, AD can be excluded with high degree of certainty. The intermediate risk group will only encompass around one third of patients, which substantially will reduce the need for confirmatory CSF or PET testing at the specialist clinic, and thus cost savings for the society.
The study is published in the journal Nature Aging.
More information: Brum, W.S. et al, A two-step workflow based on plasma p-tau217 to screen for amyloid β positivity with further confirmatory testing only in uncertain cases, Nature Aging (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s43587-023-00471-5 www.nature.com/articles/s43587-023-00471-5