This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Revealing the roles of TLR7, a nucleic acid sensor for COVID-19, in pan-cancer
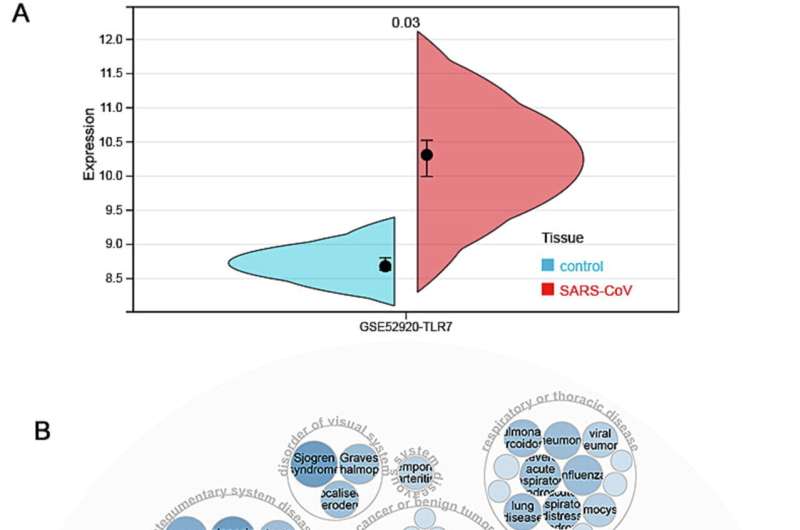
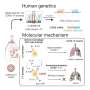
Researchers have discovered toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7), a nucleic acid sensor within the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus, to be aberrantly expressed in many types of cancers. However, its expression pattern across cancers and association with COVID-19 (or its causing virus SARS-CoV-2) has not been systematically studied.
The paper is published in the journal Biosafety and Health.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a disease mainly characterized by damage to the respiratory system caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Recent studies suggest that cancer was a risk factor for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
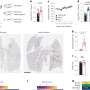
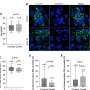
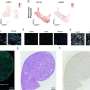
In this study, the authors of this article employed a computational framework to comprehensively study the roles of TLR7 in COVID-19 and pan-cancers at genetic, gene expression, protein, epigenetic, and single-cell levels. As a result, they found TLR7 expression to be higher in the lungs of mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 than in those of the control group.
This study reveals the roles of TLR7, a nucleic acid sensor for COVID-19 in pan-cancer. These findings could be significant in efforts to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and alleviate cytokine storms in infected cancer patients.
More information: Zhijian Huang et al, Revealing the roles of TLR7, a nucleic acid sensor for COVID-19 in pan-cancer, Biosafety and Health (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.05.004