This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Significant link found between paternal depression and an increased risk of mental health issues in offspring
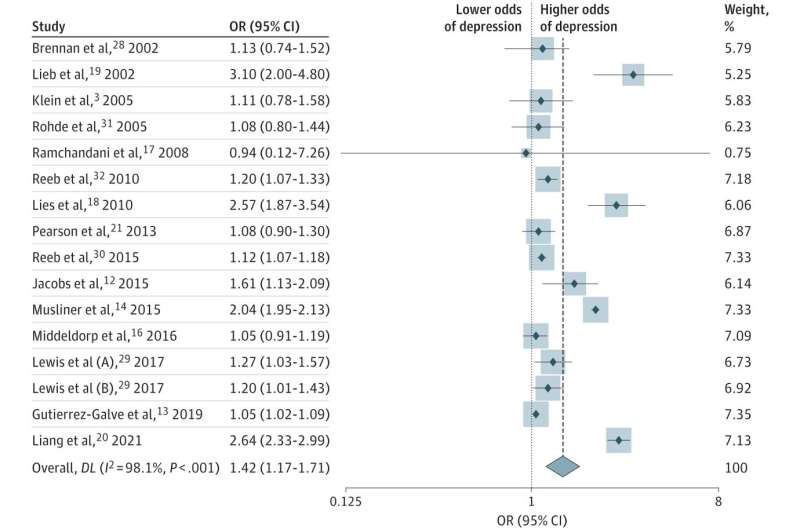
A global review of studies involving more than 7 million fathers, including Australians, and their children has confirmed a significant link between paternal depression and an increased risk of mental health issues in their offspring.
The Curtin University-led review looked at 16 international studies undertaken between 2002 and 2021, and found children faced a 42% higher risk of depression if their father was depressed.
Lead author Dr. Berihun Dachew, a post-doctoral research fellow in epidemiology from the Curtin School of Population Health, said the review explored the connection between depression in fathers and their children.
"This review highlights the need for a more comprehensive approach that acknowledges the influence of the paternal parents' mental health on the overall mental well-being of the family," Dr. Dachew said.
"We found when fathers had more severe depression requiring clinical assistance, the risk for their children developing depression was even stronger, as opposed to dads with milder symptoms of feeling down."
Dr. Dachew said people's genetic predisposition, or the capacity we are born with to learn language and concept of self, parenting style and interaction, as well as family environment and stress, might explain the links researchers observed.
"While there is an increasing awareness of the role paternal depression can have in child development and later psychosocial outcomes, current interventions for preventing adolescent depression focuses largely on mothers," Dr. Dachew said.
"Our findings highlight the significance of adopting a family-focused approach that addresses both maternal and paternal mental health issues to mitigate the negative effects on children's well-being."
Senior author and Head of the Curtin School of Population Health, Professor Rosa Alati, said the findings emphasized the importance of early intervention and support for father experiencing depression.
"Considering the prevalence of paternal depression and the increasing involvement of fathers in childcare, it is crucial to incorporate paternal mental health when addressing the well-being of offspring," Professor Alati said.
"By recognizing the impact of paternal depression on children, policymakers, health care professionals and support services should work towards implementing strategies that promote mental wellness in fathers and provide resources to mitigate the risk of depression in their children."
The research is published in the journal JAMA Network Open.
More information: Berihun Dachew et al, Paternal Depression and Risk of Depression Among Offspring, JAMA Network Open (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.29159. jamanetwork.com/journals/jaman … /fullarticle/2808380