This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Alcohol and other drug use more prevalent in non-car injuries, shows study
A higher percentage of people admitted to hospital for falls, self-harm and violence have used alcohol and other drugs than drivers admitted after car crashes, new research has found.
The Monash University-led study, believed to be Victoria's first to analyze the alcohol and other drug use of trauma patients with non-transport injuries, has prompted calls for more prevention efforts.
Published in Emergency Medicine Australasia, the project analyzed valid pathology tests from 1,248 people treated by The Alfred trauma team for serious non-transport injuries from 1 July 2021 to 31 December 2022.
Of those admitted to the hospital, 37.4% tested positive for alcohol and other drugs. This included 68.7% of those injured due to violence, 47.2% hurt by self-harm and 32.6% of those who'd had falls.
This compared to a previously reported figure of 28.7% of injured car drivers testing positive to alcohol and other drugs after hospital admission.
First author and Monash School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine Ph.D. candidate Georgina Lau said the figures showed that prevention efforts should also target non-transport incidents such as falls, self-harm and violence.
"Traditionally, the focus of prevention efforts for alcohol and drug-related injuries has focused almost exclusively on drink and drug driving," Lau said.
"Meanwhile, the role of alcohol and other drugs in non-transport injury causes such as falls, self-harm, and violence, has been largely overlooked in existing national strategies and prevention efforts, even though these causes account for 66% of serious injuries.
"The results of this study demonstrate that alcohol and other drugs are substantially more common in these non-transport injury causes."
Conducted with several Alfred Health emergency and trauma experts, the study also found that of those who presented to The Alfred with serious injuries from a non-transport event:
- Alcohol was the most commonly detected substance (25.1%), followed by cannabinoids, (14.1%), benzodiazepines, (13.4%), amphetamine-type substances (10.9%), opioids (3.8%) and cocaine (2.3%).
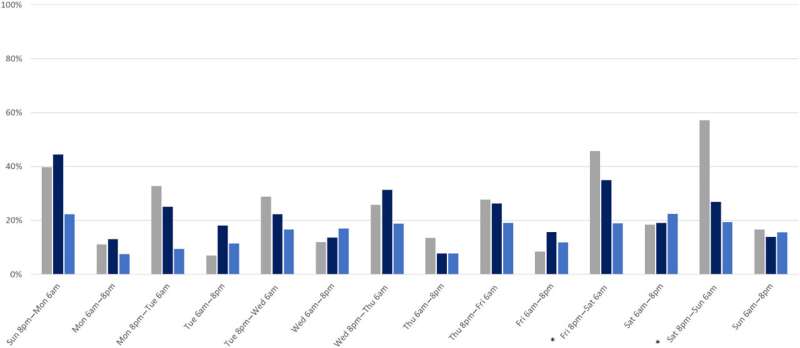
- 61.8% of those injured on Friday and Saturday nights tested positive for alcohol or other drugs.
- 39.8% of those injured in low falls (falls from standing or a height less than one meter) and 27.6% of those injured in high falls (falls from a height more than one meter) tested positive to alcohol or other drugs. The combined figure was 32.6%.
Lau said there was limited recent knowledge about the proportion of injuries that involved alcohol and other drugs in Australia.
"Alcohol and drug-related injuries are associated with substantial costs for the people who are injured, as well as for the health care system and the economy," she said.
"This study has provided novel and up to date insights into the high proportion of injuries that involve alcohol and other drugs. These findings are crucial for informing future research and identifying areas where we can focus future injury prevention strategies."
Professor Biswadev Mitra, co-author and Emergency Physician at The Alfred Emergency & Trauma Center said that the exposure to alcohol and other drugs added a substantial degree of complexity to assessing and managing injured patients.
"Highlighting the association of alcohol and other drugs with major trauma is an essential step to empowering people with the knowledge of the high risks and cost of substance use," he said.
Senior author and Head of Sustainable Mobility and Safety Research, Associate Professor Ben Beck, said the findings highlighted the substantial role of alcohol and other drugs in injury events.
"There is a clear need to prioritize the prevention of alcohol and other drug-related injuries in national strategies and to develop countermeasures to prevent these injuries from occurring," he said.
More information: Georgina Lau et al, Prevalence of alcohol and other drug detections in non‐transport injury events, Emergency Medicine Australasia (2023). DOI: 10.1111/1742-6723.14312