This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
DPP4 inhibitors for target therapy resistance in renal cell carcinoma
A new editorial paper titled "Potential repurposing of DPP4 inhibitors for target therapy resistance in renal cell carcinoma" has been published in Oncotarget.
In their new editorial, researchers Kuniko Horie and Satoshi Inoue from Saitama Medical University and Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Geriatrics and Gerontology discuss renal cell carcinoma (RCC)—a major adult kidney cancer, which is often incidentally discovered as an asymptomatic disease on imaging in the developed countries.
RCC has the most fatal disease among urological cancers, as a recent 5-year relative survival rate in the U.S. (2009–2015) is less than 80%. While RCC is known as a cancer resistant to chemo- and radiotherapies, the prognosis of RCC has been remarkably improved after the clinical application of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immunotherapy.
The rationale for the efficacy of TKIs in RCC is mainly based on the angiogenetic status, particularly in clear cell RCC (ccRCC) that is the most common type of RCC (70–75% of RCC), in which the loss of function mutation of Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor gene activates hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathways.
The first-line TKIs that predominantly target VEGF receptor (VEGFR) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) (e.g., sunitinib and sorafenib) have been clinically used since late 2000s, and the second-line TKIs such as cabozantinib, which targets more receptor tyrosine kinases including MET and TAM kinases as well as VEGFR, have been further applied to the treatment of advanced RCC since early 2010s in which the first-line TKIs are ineffective.
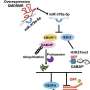
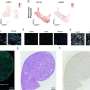
"In our recent study, we established a panel of patient-derived ccRCC spheroid cultures with the enhancement of cancer stemness gene signature including DPP4. Focusing on TKI sunitinib sensitivity, we demonstrated that DPP4 inhibition increased sunitinib efficacy in DPP4-high RCC spheroids and DPP4 was upregulated in sunitinib-resistant RCC cells," the researchers explain.
More information: Kuniko Horie et al, Potential repurposing of DPP4 inhibitors for target therapy resistance in renal cell carcinoma, Oncotarget (2023). DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28463