This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Liver cancer and severe liver disease found to be more common if a close relative has fatty liver disease
Close relatives of people with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease have a higher risk of developing liver cancer and dying from liver-related diseases, according to a national study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden published in the Journal of Hepatology. This means that family members could also benefit from the lifestyle advice that is currently only given to patients, the researchers conclude.
People with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MASLD, formerly known as NAFLD) have an elevated risk of developing and dying from liver cancer. MASLD is now the main reason why the number of people developing liver cancer has risen so sharply. However, researchers at Karolinska Institutet now show that close relatives and partners also have an increased risk of developing liver cancer and advanced liver disease.
May benefit from early screening
"Our findings indicate that patients with MASLD should not be treated separately," says the study's first author Fahim Ebrahimi, doctor and researcher at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet. "Indeed, recommendations for lifestyle changes should be given to their family members as well. Our study also suggests that relatives with metabolic risk factors such as diabetes mellitus may benefit from early screening for MASLD."
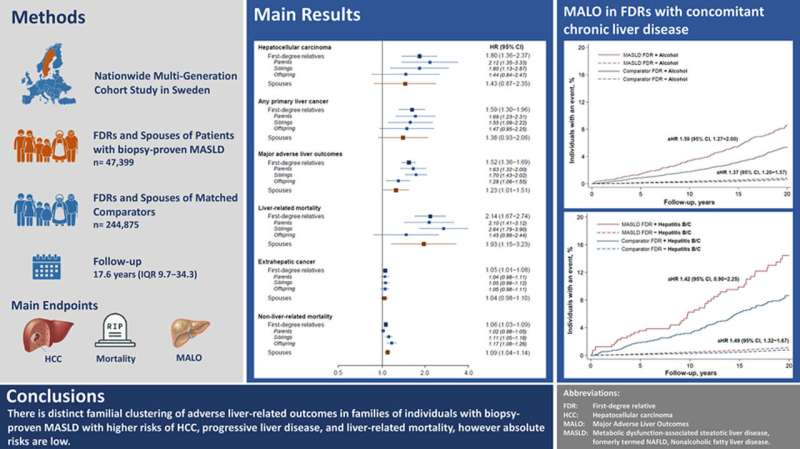
The researchers based their study on the ESPRESSO cohort, which contains data on all liver biopsies taken in Sweden from 1965 up to the present. They identified almost 12,000 people with biopsy-proven MASLD. After matching each person with up to five comparators from the general population they identified first-degree relatives (parents, siblings and children) and partners for both groups. The study included nearly 250,000 first-degree relatives and 57,000 partners.
Followed for up to 50 years
Over an average follow-up period of 17.6 years, with some individuals being followed for up to 50 years, the researchers found that first-degree relatives of MASLD patients were 80 percent more likely to develop liver cancer than the controls. However, as liver cancer is a relatively rare disease, the absolute increase in risk is much lower: 0.11 percent over 20 years, according to the researchers.
"In other words, one in every 900 first-degree relatives of patients with MASLD will additionally develop liver cancer over a 20-year period," says senior author Jonas F. Ludvigsson, professor at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet. "So, the absolute risk is very small, but still relevant at a population level."
The researchers also found that partners of patients with MASLD were more likely to develop severe liver disease (such as cirrhosis) and to die from liver-related causes.
"Our findings confirm that there is a clear familial risk of MASLD and that a shared lifestyle is an important factor in its development," says Dr. Ebrahimi.
More information: Fahim Ebrahimi et al, Familial Coaggregation of MASLD with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adverse Liver Outcomes: Nationwide Multigeneration Cohort Study, Journal of Hepatology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.08.018