This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Parents, especially mothers of young, dependent children affected most by COVID-19 lockdown
Who fared worst when isolated during Melbourne's hard and long COVID-19 lockdown? A University of Sydney-led research team has found that parents, in particular mothers of young, dependent children, were hit hardest.
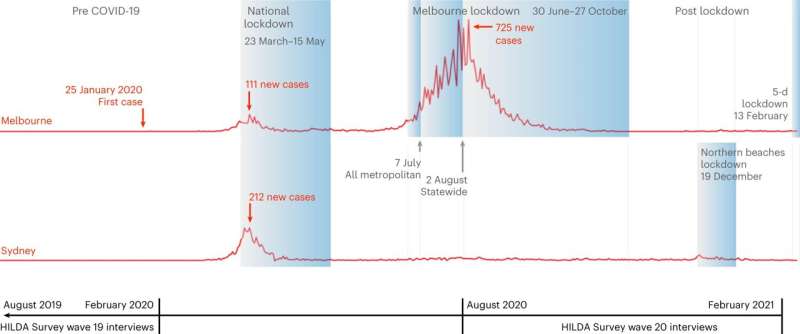
In their paper published in Nature Human Behaviour, the authors of the study reveal that during Melbourne's 111-day long first lockdown in 2020 it was mothers who experienced significant drops in their mental and general health and increases in their perceptions of loneliness, despite them feeling safer and getting more exercise.
"Surprisingly, we found few significant effects for other vulnerable demographics, such as young people, people living alone, or those with poor mental health," lead author, Professor Stefanie Schurer from the School of Economics, said.
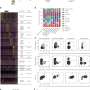
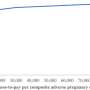
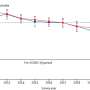
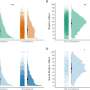
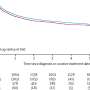
Statistically analyzing 10 years' worth of longitudinal data from the annual, national Household, Income and Labor Dynamics in Australia (HILDA) Survey and comparing Melbourne—in lockdown, with Sydney—not in lockdown, the researchers found mothers' declines in mental and general health were equivalent to a 10% drop, relative to long-term averages before the lockdown. Mothers' perceptions of loneliness increased by almost 20% relative to Melbourne's long-term average. Their work hours, too, plummeted by almost six hours a week by the end of lockdown.
Mental health was worse for mothers in apartments, rather than houses, which the researchers attribute to a sense of confinement. "Our study suggests that the lockdown was really stressful for mothers with young, dependent children," Professor Schurer continued.
The researchers also found that fathers fared worse than the general population. Their work hours dropped by about four hours per week and their weekly gross salaries were AUD$280 less per week by the end of lockdown. Fathers also drank alcohol more frequently, moving from drinking once per week to about two days per week. As the end of the lockdown neared, fathers had significantly higher Body Mass Indexes, suggesting a decline in healthy habits.
Professor Schurer believes the excessive strain on families entitles them to a "pamper transfer"—a fiscal acknowledgement of their suffering from the government.
Melbourne's longest lockdown
Melbourne's longest lockdown began on 9 July 2020 and lasted 111 consecutive days. At the time, it was the second-longest lockdown in the world and the harshest in terms of restrictions: people were only allowed to leave their homes for one hour per day.
It was the first time a jurisdiction in the Western World imposed a lockdown before there was an official public health or financial crisis. At the time of lockdown, there were less than 100 new COVID cases per day and only a few deaths, concentrated among those aged 70 and above and mostly in residential care.
The researchers say their collaboration was driven by the experience of living in repeated lockdowns. "Melbourne's 'Zero COVID' policy, that aimed to, and did, save lives, came with major restriction of civil liberties," Professor Schurer said. "It is fair to ask who might be harmed by doing this, so that future interventions to save lives can be tailored to those most in need."
The author team acknowledged that their study is only representative for the immediate impacts of the first long and hard lockdown, and that further research is needed to determine the longer-term effects of repeated lockdowns.
More information: Stefanie Schurer et al, Quantifying the human impact of Melbourne's 111-day hard lockdown experiment on the adult population, Nature Human Behaviour (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41562-023-01638-1