This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Radio-theranostics strategy offers a powerful new tool in the fight against pancreatic cancer
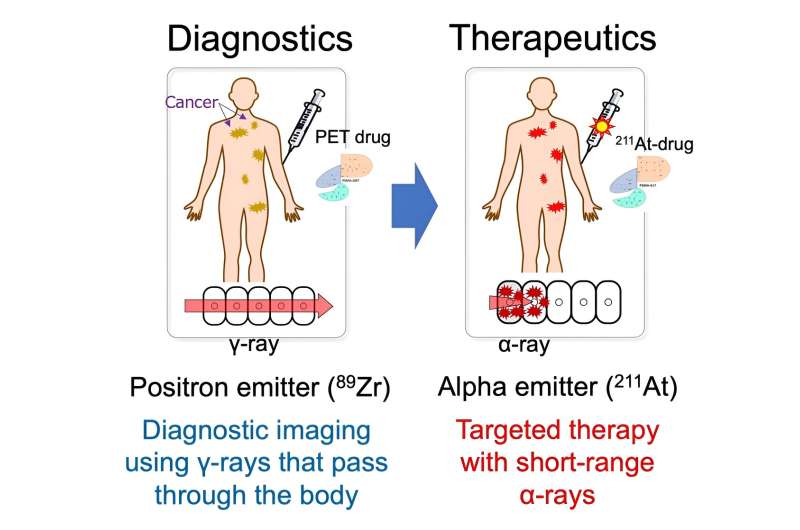
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%. Many PDAC tumors in early stage go undetected because they are not found using conventional imaging methods, including fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET) scans. To more efficiently combat this cancer, a team led by researchers at Osaka University is combining diagnostic and therapeutic procedures into a single integrated process: theranostics.
In an article recently published in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine, the team has developed a radio-theranostics strategy that uses a new radioactive antibody to target glypican-1 (GPC1), a protein highly expressed in PDAC tumors. Theranostics, particularly radio-theranostics, has been receiving increasing attention because, by radio-labeling the compounds used to target certain molecules in cancer cells, diagnosis and treatment can be carried out sequentially.
"We decided to target GPC1 because it is overexpressed in PDAC but is only present in low levels in normal tissues," explains Tadashi Watabe, lead author of the study.
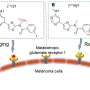
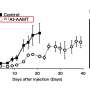
The team used a monoclonal antibody (mAb), an antibody designed to target a certain molecule, to target GPC1. The mAb could be labeled with radioactive zirconium (89Zr) or radioactive astatine (211At). They worked with a xenograft mouse model, which involved human pancreatic cancer cells being injected into a mouse that developed into a full tumor that could be experimentally treated and monitored. These mice were intravenously administered 89Zr-labeled GPC1 mAb. They were also given 211At-labeled GPC1 mAb to examine the antitumor effects.
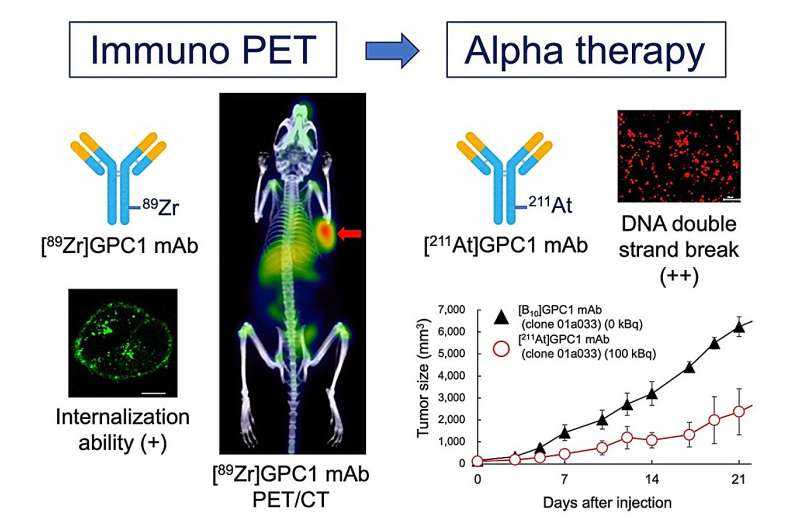
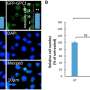
"We monitored 89Zr-GPC1 mAb internalization over seven days with PET scanning," explains Kazuya Kabayama, the second author of the article. "There was strong uptake of the mAb into the tumors, suggesting that this method could support tumor visualization. We confirmed that this was mediated by its binding to GPC1, as the xenograft model that had GPC1 expression knocked out showed significantly less uptake."
The researchers next tested this model with alpha therapy using 211At-GPC1 mAb, a method that could support radioactive label-based delivery of a therapeutic molecule to its target. Administration of 211At-GPC1 mAb resulted in DNA double-strand break induction in the cancer cells, as well as significantly reduced tumor growth. Control experiments showed that these antitumor effects did not occur when mAb internalization was blocked. Additionally, non-radiolabeled GPC1 mAb did not induce these effects.
"Both radiolabeled versions of the GPC1 mAb we examined showed promising results in PDAC," says Watabe. "89Zr-GPC1 mAb showed high tumoral uptake, while 211At-GPC1 mAb could be used for targeted alpha therapy to support suppression of PDAC tumor growth."
These highly impactful data demonstrate the potential for using a theranostics approach in PDAC, a disease in dire need of new diagnostic and therapeutic options. In the future, this could lead to early detection of PDAC with PET imaging and systemic treatment with alpha therapy.
More information: Tadashi Watabe et al, Immuno-PET and Targeted α-Therapy Using Anti–Glypican-1 Antibody Labeled with89Zr or211At: A Theranostic Approach for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma, Journal of Nuclear Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.123.266313