This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Maintenance immunosuppressive drugs tied to severe COVID-19
Maintenance immunosuppressive drugs are associated with an increased risk for COVID-19 hospitalization in solid organ transplant recipients, according to a study published online Nov. 7 in JAMA Network Open.
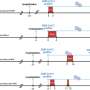
Epiphane Kolla, M.D., M.P.H., from the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products in Paris, and colleagues examined factors associated with severe COVID-19 among solid organ transplant recipients. The analysis included 60,456 participants (median age, 59 years; 63.7 percent male; 68.6 percent kidney transplants, 23.9 percent liver transplants, 8.8 percent heart transplants, and 4.6 percent lung transplants).
The researchers found that 12.7 percent of kidney, 6.4 percent of liver, 12.9 percent of heart, and 18.0 percent of lung transplant recipients were hospitalized for COVID-19. Steroids and mycophenolic acid were associated with a high risk for hospitalization in kidney transplant recipients. Tacrolimus was associated with a decreased risk for hospitalization in liver transplant recipients, while steroids and mycophenolic acid were associated with an increased risk for hospitalizations.
Cyclosporine was associated with a decreased risk for hospitalization in heart transplant recipients, while steroids, mycophenolic acid, sirolimus, and everolimus were associated with an increased risk for hospitalization. In lung transplant recipients, only steroids were associated with a high risk for COVID-19 hospitalization.
"Health care professionals should consider these results in treating solid organ transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing doses or modifying medications in some cases," the authors write.
One author disclosed ties to industry.
More information: Epiphane Kolla et al, COVID-19 Hospitalization in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients on Immunosuppressive Therapy, JAMA Network Open (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.42006
Copyright © 2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.