This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
What leads people to take action on disease prevention?
When making important decisions about disease prevention, who do you listen to? Medical institutions? Or perhaps the people around you? Your answer might reveal more about your personal circumstances than you would expect.
In a study published this month in the International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that, when taking steps to prevent the spread of disease, we are affected by certain factors surrounding us, such as where we get our information and whether we currently live under a pandemic. The study is titled "Exploration of factors associated with mask-wearing and hand disinfection in Japan after the coronavirus disease outbreak: A longitudinal study."
In response to the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, many countries implemented social measures, such as lockdowns, and mandated preventive behaviors, such as mask-wearing, for their residents. In Japan, behaviors that prevent infection, such as hand sanitizing and mask-wearing, have been left to individual discretion since the beginning of the COVID-19 outbreak.
"Since COVID-19 continues to circulate globally, it is important to determine the associations between individual characteristics and preventive behaviors to understand how to promote discretion-based preventive behaviors," explains Michio Murakami, lead author of the study. "We are particularly interested in developing a risk communication strategy for promoting infection-preventive behavior in a timely manner."
To address this, the researchers investigated the association between certain individual characteristics before and after the outbreak of COVID-19. Using 23 waves of panel data from January 2020 to January 2023, the researchers examined whether individuals consumed medical information on government or medical institution websites, whether they wore masks, and whether they disinfected their hands.
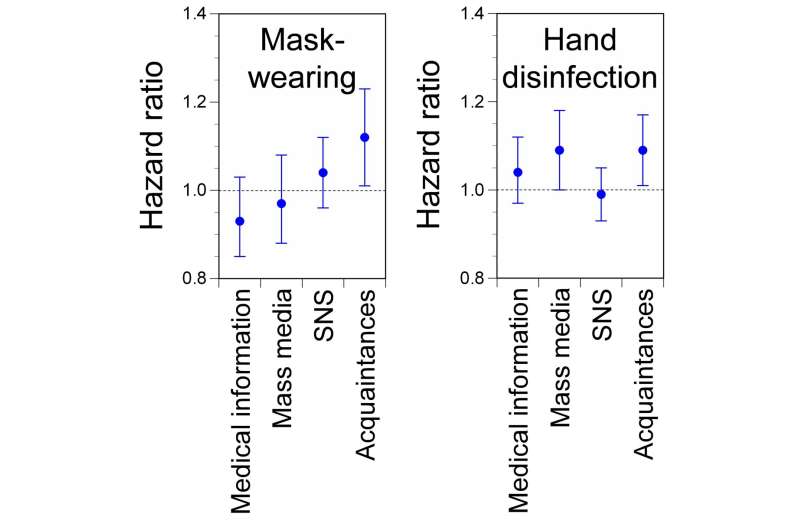
"The results were intriguing," explains Asako Miura, senior author. "We found that, while medical information had the strong effect on infection-preventive behavior before the COVID-19 outbreak, people who exchanged information with acquaintances were more likely to newly start mask-wearing and hand disinfection after the COVID-19 outbreak."
The researchers found that people who consumed medical information were more likely to wear masks and disinfect hands even before the COVID-19 outbreak. There were also slight differences in the rates of infection-preventive behavior and gender, with men less likely to implement preventive behaviors than women.
"Our findings clearly show that, in Japan, mask-wearing and hand-disinfection behaviors were the result of different information sources before and after the outbreak," says Murakami.
Given that infection-preventive behaviors protect not only against COVID-19, but also seasonal and emerging infectious diseases, the insights from this study are a valuable contribution to public health. In particular, implementing the appropriate communication strategies for certain demographics can be an effective aid to disease prevention.
More information: Michio Murakami et al, Exploration of factors associated with mask-wearing and hand disinfection in Japan after the coronavirus disease outbreak: A longitudinal study, International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.104107