This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Food insecurity among low-income adults dropped nearly 5% during pandemic-era SNAP expansion

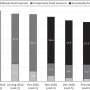
Benefits expansions during the COVID-19 pandemic may have helped to mitigate food insecurity among low-income adults. A survey of low-income adults showed that food insecurity dropped nearly 5% in 2021 compared to 2019. The findings are published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Food insecurity is a major driver of health disparities in the United States. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the federal government expanded the social safety net, including increases in spending on the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP). Little is known about how food insecurity changed among low-income adults over the course of the pandemic.
Researchers from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School used data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), a nationally representative survey from the National Center for Health Statistics, to examine food insecurity among low-income adults during versus before the pandemic.
They included 2019 as a pre-pandemic reference for both 2021 and 2022 cycles but excluded 2020 because the onset of the pandemic created challenges in conducting the survey.
The data showed that food insecurity decreased from 20.6% in 2019 to 15.5% in 2021, despite worsening unemployment and economic loss. By 2022, food insecurity rates had returned to pre-pandemic levels, but remained lower for low-income adults receiving SNAP benefits. According to the authors, these findings highlight the importance of financial relief and nutritional benefits for vulnerable populations.
More information: Food Insecurity Among Low-Income U.S. Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic, Annals of Internal Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.7326/M23-2282 б www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-2282
Editorial: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-3363