This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Dexmedetomidine cuts incidence of postpartum depression after C-section

For women with prenatal depression undergoing cesarean delivery, dexmedetomidine reduces the incidence of positive postpartum depression (PPD) screening, according to a study published online Jan. 25 in JAMA Network Open.
Yingyong Zhou, Ph.D., from The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University in Changsha, China, and colleagues conducted a randomized clinical trial involving 338 women who screened positive for prenatal depression and were scheduled for elective cesarean delivery at two hospitals to assess the efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine for prevention of PPD. A total of 338 participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive dexmedetomidine or saline, infused for 10 minutes after delivery. After infusion, sufentanil or dexmedetomidine plus sufentanil was administered for 48 hours in the control and dexmedetomidine groups, respectively.
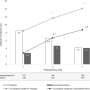
The researchers found that the incidence of positive PPD screening at seven and 42 days postpartum was significantly reduced in the dexmedetomidine group versus the control group (day 7: 12.6 versus 32.1%; risk ratio, 0.39; day 42: 11.4 versus 30.3%; risk ratio, 0.38). No significant difference was seen between the groups in terms of adverse events, but an increased incidence of hypotension was seen in the dexmedetomidine group (18.3 versus 9.5%; risk ratio, 2.15).
"Preventive administration of dexmedetomidine in the early postpartum period reduced the incidence of positive PPD screening, reduced postoperative pain, improved sleep quality, and maintained a favorable safety profile," the authors write. "Its antidepressant effect may be related to brain-derived neurotrophic factor upregulation and/or downregulation of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor."
More information: Yingyong Zhou et al, Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Postpartum Depression in Women With Prenatal Depression, JAMA Network Open (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53252
2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.