This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Modifying brain molecule relaxin-3 can potentially reduce side effects in treating anxiety, depression and more
Drugs that treat conditions like depression and anxiety often come with varying side effects, as they regulate various functions within the human body at the same time. What if these drugs could activate only the functions that target the specific conditions that they are designed to treat?
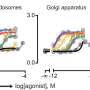
A team of researchers has found a potential way to treat these conditions with fewer side effects. Led by Professor Gavin Dawe, Head of the Department of Pharmacology at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), the team conducted modifications of relaxin-3—a neuropeptide, or molecule, found mainly in the human brain and nervous system—that regulates a wide range of physiological functions, including stress responses, appetite, mood and pain perception. When relaxin-3 is released in the brain, it binds to a target receptor RXFP3—to trigger a variety of signaling responses among the cells, which affect the body's physiological processes.
The findings are published in the journal Science Signaling.
However, as RXFP3 is involved in many different functions, a drug developed to treat certain conditions may cause unwanted side effects—because several of RXFP3's signaling pathways are activated at the same time. For example, a drug that treats depression may cause adverse effects related to another function, such as feeding behavior, which is related to eating disorders and obesity.
The receptor has also been demonstrated in much existing research, including earlier work by Prof. Dawe, to be a potential new target for drugs to treat these conditions. To develop better drug treatments with fewer side effects, the key is to activate only specific signaling pathways of RXFP3 that target specific conditions.
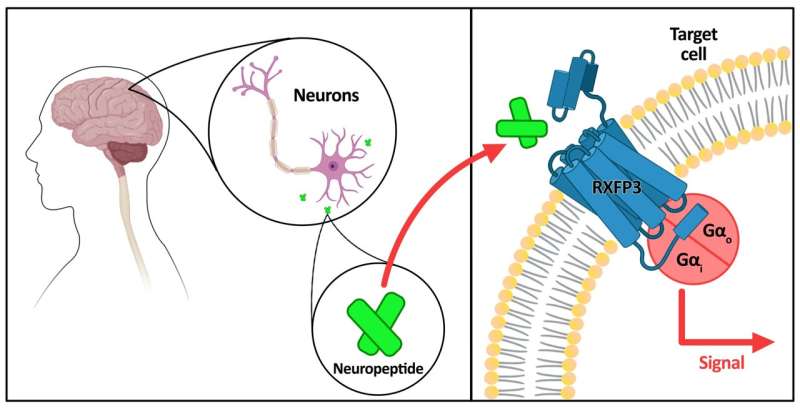
Prof. Dawe's team modified the relaxin-3 molecules, such that they activated only a part of the RXFP3 response in their interaction, instead of all the different signaling pathways. Their work is the first discovery that modifications of relaxin-3 can lead to selective activation of some RXFP3-led signaling pathways, which is a mechanism known as biased agonism.
Prof. Dawe said, "Our study has pointed to potential ways of developing drugs by modifying relaxin-3, or other neuropeptides, that can selectively activate specific functions within the body. This is important as it means drugs could be designed to have more specific effects and less undesired adverse effects, making them more effective in managing a range of conditions like anxiety, depression, eating disorders, obesity, and addiction."
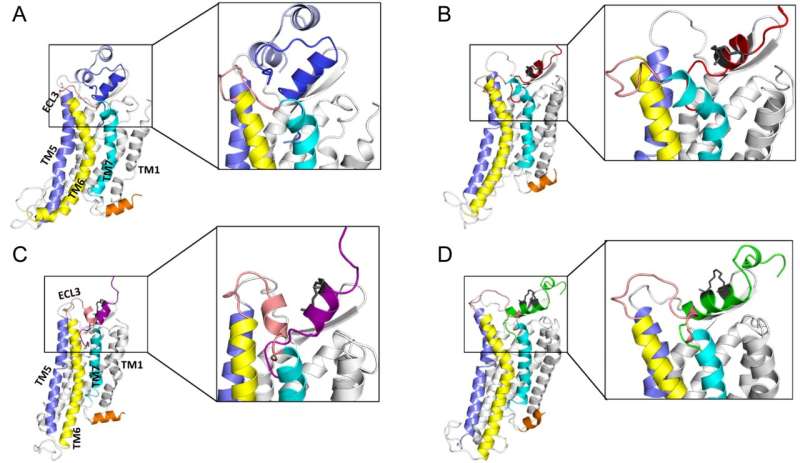
Through a technique known as peptide stapling, the research team modified the B-chain of relaxin-3, replacing blocks of amino acids within them with artificial ones that introduce "chemical bridges" between them. Alone, the B-chain is highly flexible and can twist and bend into many different shapes, reducing its ability to be stabilized for more effective binding and activation of the receptor RXFP3.
The stapling process locks the shape of the specific B-chain in relaxin-3, stabilizing it for a more efficient interaction with the receptor RXFP3, where it triggers certain signaling pathways in the brain that affect the body's physiological functions.
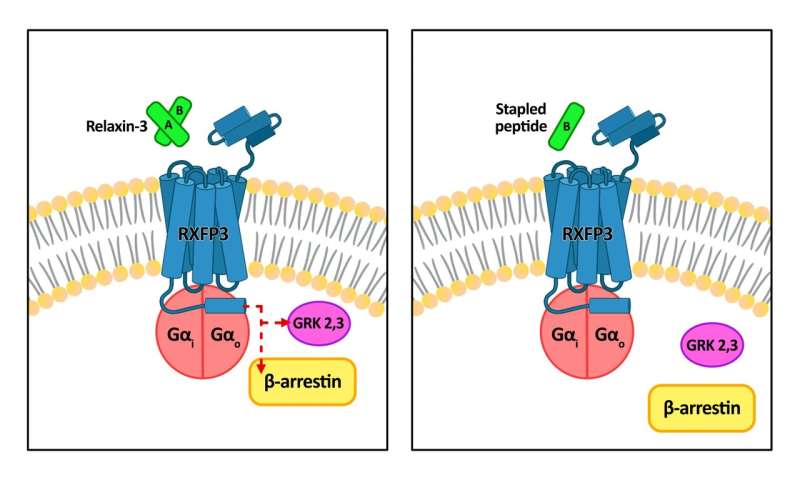
Dr. Tharindunee Jayakody, first author of the study and Ph.D. alumna of the Department of Pharmacology at NUS Medicine, said, "We are at very early stages in terms of the journey in making clinically useful drugs. However, the promising findings from our study are a significant step in our aspiration to separately design stapled peptides that have selective effects on anxiety, depression, eating disorders and addiction. Our collaborative work would also strive to understand how proteins like RXFP3 function at a molecular level, with the help of biased agonists."
Jayakody is leading a team of researchers to understand the molecular properties of proteins such as RXFP3 at the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka, where she is a lecturer in biochemistry and molecular biology.
With the conclusion of the study, the research team plans to use different stapled peptides to understand how the signaling functions, activated by the interactions between relaxin-3 and RXFP3, affect the body's physiological functions and human behavior.
More information: Tharindunee Jayakody et al, Mechanisms of biased agonism by Gα i/o -biased stapled peptide agonists of the relaxin-3 receptor, Science Signaling (2024). DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.abl5880