This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Greener streets linked to better sleep
Living on a greener street or having views of blue spaces from your home will help you sleep for longer.
New research across 18 countries, led by the University of Exeter's European Centre for Environment and Human Health, found that living on greener streets—those with visible grass, trees, and vegetation—is linked to better sleep. While past research has found a connection between green spaces and better sleep, this is the first time several different types of natural environments have been analyzed across different countries.
Lack of sleep, typically defined as fewer than six hours a night, is a significant public health issue in industrialized countries, affecting around 16 percent of UK adults. Poor sleep is linked to a range of adverse health and well-being outcomes, including non-communicable diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions, as well as increased risks of mortality.
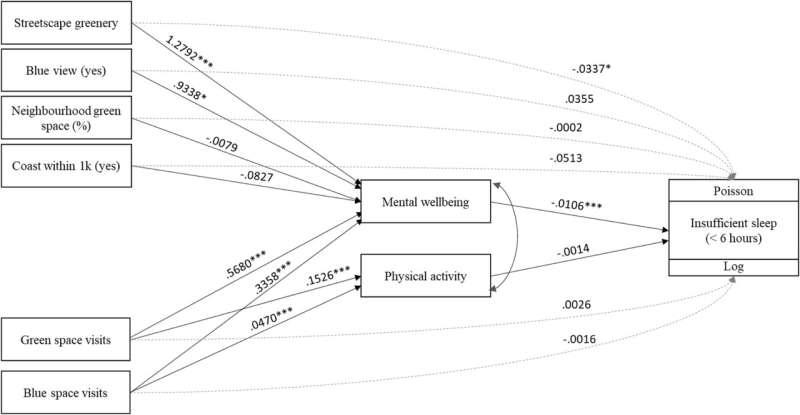
Lead author Dr. Leanne Martin from the University of Exeter's European Centre for Environment and Human Health said, "People that lived in greener streets reported better mental health, which was the driving factor behind getting a better night's sleep."
"Streetscape greening initiatives already exist in urban cities to tackle environmental risks like flooding and heat island effects, but our findings suggest policymakers should extend that to residential areas to support public health by promoting healthier sleep habits."
Data was used from over 16,000 people across 14 European countries, as well as Australia, Canada, the U.S., and Hong Kong, as part of the BlueHealth International Survey (BIS)—a cross-sectional survey co-ordinated by the European Centre for Environment and Human Health in Penryn. Respondents were asked about the amount of greenery on their street, whether they had views of rivers, lakes, and coasts (collectively known as blue spaces) from home, how much leisure time they spent in natural spaces, as well as their mental health and how many hours they slept a night.
The research found individuals who lived in greener streets or had views of blue spaces from their homes tended to report better mental health, which in turn was associated with healthier amounts of sleep. Individuals who spent more recreational time in green and blue spaces also reported better mental health and healthier sleep durations.
Overall, results found that 17 percent of people who lived on green streets reported getting fewer than six hours of sleep a night, compared to 22 percent of those who did not live on green streets.
Co-author of the study, Dr. Mathew White, from the University of Vienna, said, "While a five percent difference may seem small, these findings are comparable to the difference in sleep between people who are coping on their present income and those under financial strain. With money worries widely recognized as an important determinant of sleep, we think this demonstrates street greenness should be recognized by governments as an important public health issue."
The paper is published in the journal Environmental Research.
More information: Leanne Martin et al, Mechanisms underlying the associations between different types of nature exposure and sleep duration: An 18-country analysis, Environmental Research (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118522