This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New clinical practice guideline provides evidence-based recommendations for age-related hearing loss
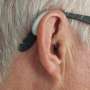
The American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO-HNSF) has published "Clinical Practice Guideline: Age-Related Hearing Loss" in Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. This clinical practice guideline (CPG) sheds lights on a global public health problem affecting approximately 466 million people worldwide and identifies quality improvement opportunities and provide clinicians trustworthy, evidence-based recommendations regarding the identification and management of age-related hearing loss (ARHL) in patients 50 years and older.
"Age-related hearing loss is underdiagnosed and undertreated despite being the most common sensory deficit in the aging population. With almost 50% of the population over 75 reporting hearing loss, having a clinical practice guideline allows all clinicians to provide better health care to those with hearing loss based on research and best practices. Not only does this CPG provide screening recommendations and management of the hearing loss, it also educates clinicians and care partners how to communicate with those suffering from hearing loss," said Betty S. Tsai Do, MD, the CPG Development Group Chair.
ARHL is the most common sensory disorder in the older population. Between ages of 65 to 74, one in three adults experiences hearing loss. ARHL is a type of hearing loss that occurs over time as individuals age. It develops gradually and symmetrically, meaning it affects both ears similarly and is associated with various sociodemographic factors and health risks including dementia, depression, cardiovascular disease, and falls. It is caused by both genetic and environmental factors such as exposure to loud noises, medication that can harm the ears, cigarette smoking, and alcohol consumption.
This guideline presents clinicians with an evidenced-based framework, which includes 11 evidenced-based Key Action Statements (KAS), to prioritize identifying patients at risk of ARHL as well as managing it.
"I am excited to see a key action statement focusing on social determinants of health and how it impacts access and patient preferences on the management of hearing health care. The focus of individualized health care is the future of medicine, and as such, it is important that this CPG incorporated that into the recommendations," shared Dr. Tsai Do.
The ARHL CPG recommends that all patients aged 50 and above should be screened for hearing loss because detecting hearing loss early and taking appropriate steps can help minimize the negative effects associated with untreated hearing loss.
"Our guideline development group used the AAO-HNSF methodology to create evidence-based recommendations on the management of age-related hearing loss. We hope that the CPG will be useful in improving awareness and decreasing the morbidity of untreated age-related hearing loss in an effort to improve a patient's overall health and quality of life," said Dr. Tsai Do.
The guideline development group (GDG) consisted of experts in otolaryngology (ear, nose, and throat), otology (ear), audiology (hearing), neurology (nervous system, including the brain), geriatrics (care of aging population) and primary care. The group also included a consumer representative, a public health expert, and staff members from the AAO-HNSF.
More information: Clinical Practice Guideline: Age-Related Hearing Loss, Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery (2024). DOI: 10.1002/ohn.750