This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Little guidance exists for treating inpatients with asymptomatic high blood pressure, review finds
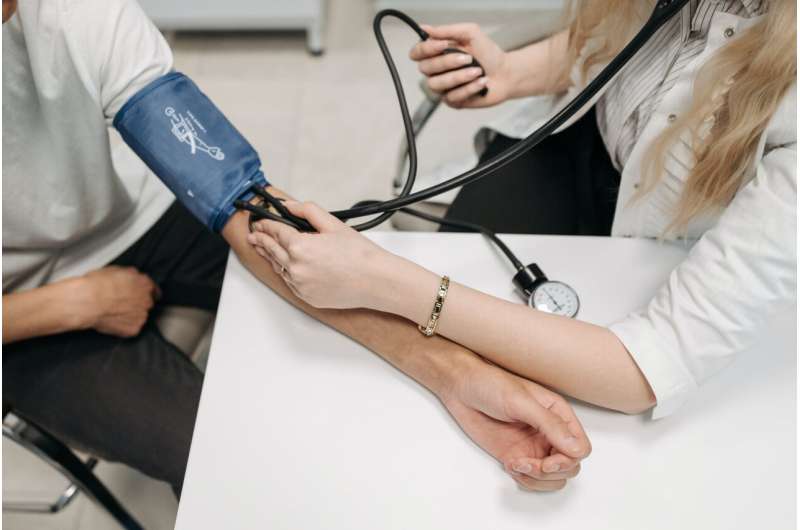
A systematic review of 14 clinical practice guidelines found that guidance on inpatient management of elevated blood pressure (BP) without symptoms is lacking. According to the authors, this lack of guidance may contribute to variable practice patterns. The review is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Management of elevated blood pressure (BP) during hospitalization varies widely, with many hospitalized adults experiencing BPs higher than those recommended for the outpatient setting. The benefits of intensive inpatient antihypertensive treatment have not been demonstrated, and there are no randomized trials of inpatient BP management.
Researchers from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, University of California San Francisco, and the University of Pittsburgh conducted a systematic review of 14 clinical practice guidelines for inpatient management of elevated BP without symptoms.
Of these guidelines, 11 provided broad BP management recommendations, and one each was specific to the emergency department setting, older adults, and hypertensive crises.
The authors found that recommendations focused on management of hypertensive emergencies and did not discuss transitional management of BP upon discharge.
In contrast to the paucity of inpatient recommendations, the authors found that guidelines consistently specified outpatient BP goals, thresholds and preferred classes for pharmacologic treatment, and follow-up duration and provided recommendations specific to patients with various comorbidities and geriatric conditions.
According to the authors, there is an urgent need for pragmatic clinical trials to fill knowledge gaps for the management of elevated BP in hospitalized adults as well as a need for the development of inpatient BP clinical decision-making frameworks that address the unique issues posed by hospitalization and care transitions.
More information: Annals of Internal Medicine (2024). www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-3251