This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study finds being overweight is associated with alterations in brain pulsations
A recent study from the University of Oulu, Finland, reveals that high body mass index (BMI) is associated with changes in physiological brain pulsations. These pulsations play a crucial role in maintaining brain fluid circulation and the clearance of metabolic waste from the brain.
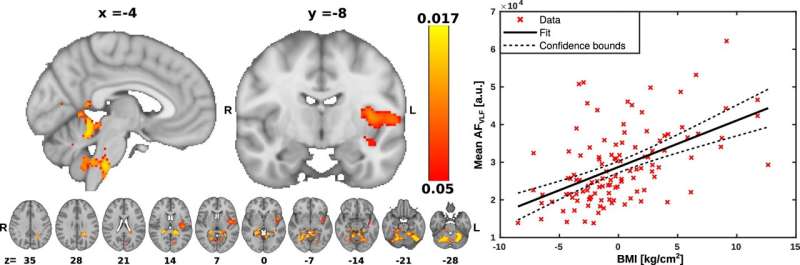
The brain exhibits three types of pulsations: cardiac driven by the heartbeat, respiratory linked to breathing cycles and vasomotion related to rhythmic blood vessel oscillations.
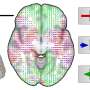
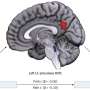
In the latest study by the Oulu Functional Neuroimaging (OFNI) research group at the University of Oulu, published in the International Journal of Obesity, it was found that a high BMI particularly intensifies pulsations related to respiration in the brain. At the same time, pulsations caused by arteries in the pituitary gland and hypothalamus region decrease, while arterial vasomotor waves increase slightly.
The findings suggest that being overweight may disrupt vital metabolic processes and homeostasis in the brain.
The study used ultrafast MREG imaging to examine the brain activity of 115 healthy adults at rest. Additional factors such as gender, age, and blood pressure, known to correlate with BMI, were taken into account, enhancing the reliability of the findings. The results indicate that a high BMI significantly impacts brain pulsations throughout the brain.
Researchers emphasize the need for greater consideration of the effects of being overweight on the brain in both scientific research and clinical practice.
"Overweight is a risk factor for many brain and cardiovascular diseases. These research findings help us understand how overweight affects brain function and the associated neurological risks.
"These observations may also help develop new diagnostic tools and treatment methods for conditions such as memory disorders, which are often associated with overweight," says Doctoral Researcher Lauri Raitamaa.
More information: Lauri Raitamaa et al, Association of body-mass index with physiological brain pulsations across adulthood – a fast fMRI study, International Journal of Obesity (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41366-024-01515-5