This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Scientists harness ultrasound for drug delivery and tissue implantation
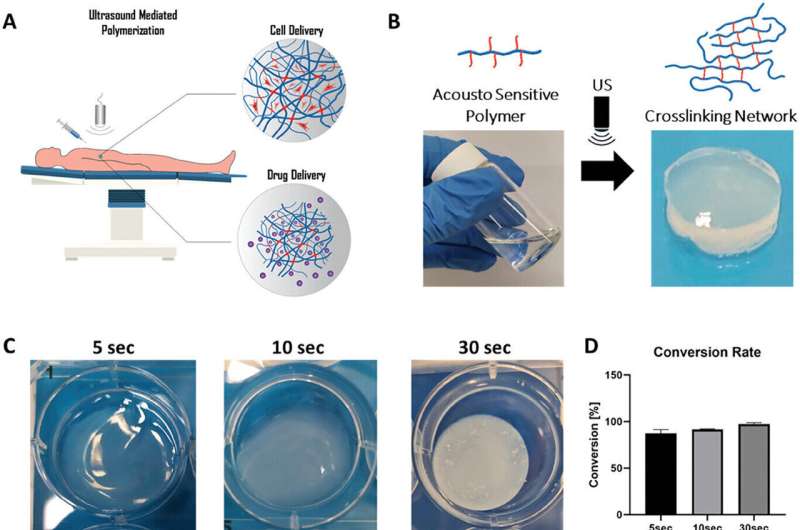
Research presents an advance in drug delivery and tissue implantation assisted by ultrasound, developed by researchers from the Technion Faculty of Biomedical Engineering. The work is published in the journal Small Methods.
Prof. Shulamit Levenberg's research group has developed an innovative non-invasive method for bio-printing live cells and tissues deep within the body using external sound wave irradiation. The research team includes postdoctoral fellow Dr. Lior Debbi, who completed all of his academic degrees at the Technion, and Majd Machour, a doctoral student in the MD/Ph.D. program.
Many biomedical applications require precise delivery of biocompatible materials for various purposes such as localized drug release, grafting of tissues, and implantation of engineered cells and tissues for organ regeneration. Currently, highly invasive surgeries are the norm, and are accompanied by risks including infection, tissue damage, and long healing periods.
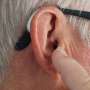
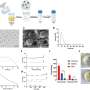
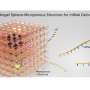
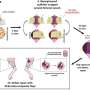
In the researchers' innovative method, cells or drugs are delivered within a biological fluid ink directly to the treated area deep within the body through direct injection or catheterization. Subsequently, the engineered tissue is printed using sound waves emitted from an external ultrasonic transducer. Thus, engineered tissue can be built deep within the body without exposing the treated site.
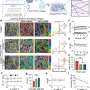
The versatility of the new technology is demonstrated in contexts such as local cell transplantation, continuous localized drug delivery over time, and three-dimensional bioprinting. The mechanical properties of the grafts can be tailored according to the target tissue and the desired drug release rate.
More information: Lior Debbi et al, Ultrasound Mediated Polymerization for Cell Delivery, Drug Delivery, and 3D Printing, Small Methods (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202301197