This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
External ventricular drainage timing in traumatic brain injury may result in better long-term functional outcomes

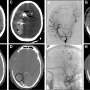
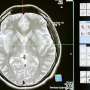
A study in the Journal of Neurotrauma shows that in patients with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) that need an external ventricular drain (EVD) insertion to control intracranial hypertension, early (
The investigators compared 6-month neurological outcomes between patients with moderate to severe TBI who received early EVD insertion versus later (more than 24-hours after injury) EVD insertion. The results showed that late EVD insertion was associated with an increased risk of death or severe disability at 6-months follow-up.
"Our study findings support the hypothesis that earlier EVD insertion may lead to improved functional neurological outcomes following m-sTBI and imply that earlier use of an EVD (within 24-hours) is likely to be more effective in the management of m-sTBI, as opposed to a later 'rescue' intervention," stated the investigators.
"Using pooled data from several different studies, these researchers found that early insertion of external ventricular drains in patients with moderate or severe traumatic brain injury was associated with better six-month outcomes than late insertion.
"These exciting results open up new directions for future research and may already impact current management of these patients," says Alex Valadka, MD, Deputy Editor of Journal of Neurotrauma, from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
More information: Jonathon D. Taylor et al, Association Between Early External Ventricular Drain Insertion and Functional Outcomes 6 Months Following Moderate-to-Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Journal of Neurotrauma (2024). DOI: 10.1089/neu.2023.0493