This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Researchers focus on placental amino acid transport to investigate causes of fetal growth disorders
Common complications of pregnancy affecting fetal size may be caused by irregularities in the transport of amino acids across the placenta—a finding with therapeutic implications. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and fetal overgrowth affect 15%–20% of pregnancies worldwide.
Abnormal fetal growth is strongly linked to the development of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease in later life. Placental transport of essential amino acids is decreased in human IUGR and increased in fetal overgrowth, but whether this was a cause or consequence was unclear.
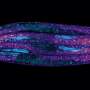
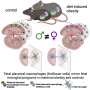
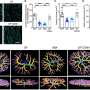
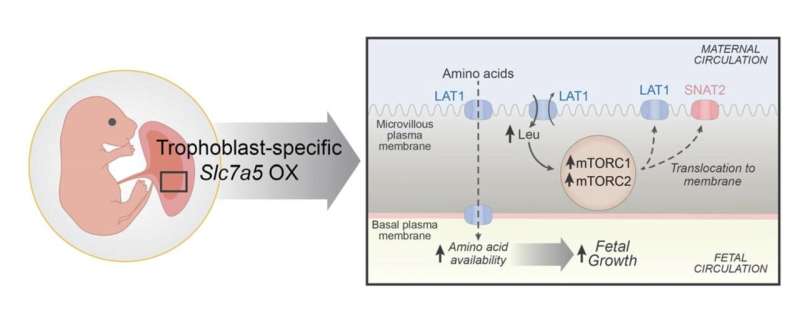
Fredrick Rosario-Joseph and colleagues created a line of mice in which the trophoblast—the main cell type in the placenta responsible for the transport of nutrients to the fetus—overexpresses a gene known as Large Neutral Amino Acid Transporter Small Subunit 1 or Slc7a5, which codes for proteins that move essential amino acids across the placenta.
The authors hypothesized that overexpressing Slc7a5 would increase fetal growth, showing a direct mechanistic link between the transport of amino acids and these common fetal conditions. Indeed, the mice bred to overexpress Slc7a5 had placentas that were on average 10% bigger and fetuses that were on average 27% bigger than control mice.
According to the authors, the results could help inform therapeutics that could not only help prevent or treat pregnancy complications, but also improve the lifetime health of the next generation.
More information: Fredrick J Rosario et al, Trophoblast-specific overexpression of the LAT1 increases transplacental transport of essential amino acids and fetal growth in mice, PNAS Nexus (2024). academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/art … 93/pnasnexus/pgae207