This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Building new bones with help from 3D printing
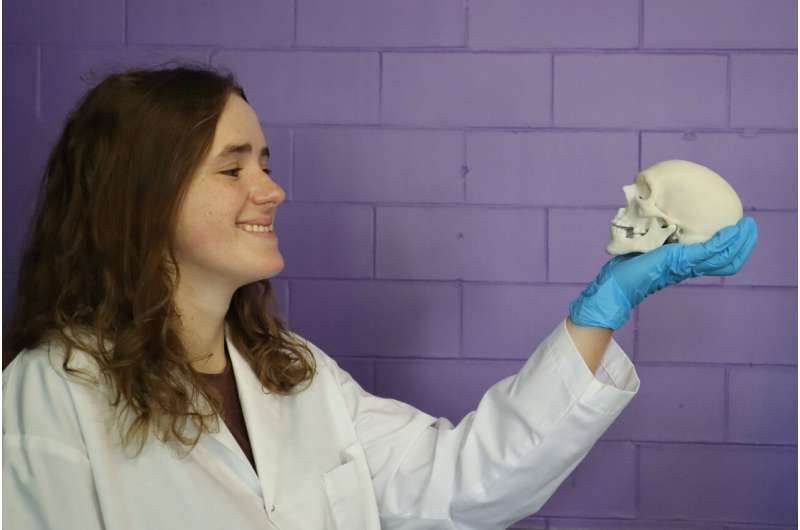

A research team from the University of Waterloo has developed a new material that shares many of the same traits as bone tissue. Using it in 3D printers provides a new and innovative treatment option for patients undergoing major skeletal repair and reconstructive surgery.
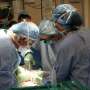
Surgical reconstruction in these cases currently involves metal implants and donated bone. Surgeons request a specific size and type from tissue banks to best match their patient's anatomy, but it's rarely a perfect fit. A recipient's body may also reject donated bone.
To solve these problems, this new biopolymer nanocomposite material can be 3D-printed into a customized bone graft engineered to meet a patient's unique needs. It may also eliminate the need for metal plates, reduce the risk of infection, and increase the chance that the patient's body will successfully accept the graft.
The paper, "In vitro evaluation of bone cell response to novel 3D-printable nanocomposite biomaterials for bone reconstruction," was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A.
"We've created a material that is strong, 3D-printable and compatible with a potential to become new bone tissue," said lead researcher Dr. Thomas Willett, a professor in the Department of Systems Design Engineering and director of the new biomedical engineering graduate program.
"With this technology, we can achieve the patient-specific geometry needed to reconstruct bone defects with greater success."
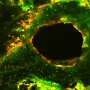
The material combines nanoparticles that mimic the composition of bone minerals and help strengthen the material. Ultimately, the team hopes bone cells will grow and replace biopolymer nanocomposite with new bone. The body will then excrete the biopolymer nanocomposite.
"Our work is currently focused on advancing our biopolymer nanocomposite's functional robustness as an implant and its ability to be replaced with living bone over time," said Elizabeth Diederichs, Waterloo Ph.D. candidate. "The goal is for this material to reduce a patient's need for repeated operations after undergoing bone reconstruction surgery."
The team performed successful tests on bone-cell compatibility in collaboration with Dr. Maud Gorbet, a professor in Waterloo Engineering and director of the biomedical engineering undergraduate program.
"Any material implanted in the body elicits a response," Gorbet said. "Our tests show that the biological response of bone cells to our biopolymer nanocomposite outperforms traditional methods. They're adhering, proliferating and retaining their behaviors, which is very exciting."
The researchers are seeking funding for additional trials and regulatory approvals to develop the technology for clinical use.
More information: Zahra Haghpanah et al, In vitro evaluation of bone cell response to novel 3D‐printable nanocomposite biomaterials for bone reconstruction, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A (2024). DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.37719