This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Reading your biological age in your blood or saliva? It's not as simple as that, study shows
How old are you, really? Your chronological age is the number of years you have been alive. Your biological age is how old your cells are, which scientists believe may better assess one's age-related health and disease risk.
People biologically age at different rates, depending on genetic and environmental factors, so that a person's chronological age does not necessarily match their biological age.
In recent years, direct-to-consumer biological age tests have become increasingly accessible and popular as interest has increased in this nascent science.
Many of these tests work by looking at distinct changes to the DNA in a patient's blood or saliva. These changes become more abundant as cells age, a phenomenon known as the "epigenetic clock." Importantly, though, it is currently unknown if the epigenetic clock advances at a similar pace in the about 200 different cell types in the human body.
A study by Konrad Hochedlinger, Rebecca Gorelov and colleagues from Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, U.S., published in Stem Cell Reports, aims to shed light on this question, asking how the presence of stem cells within a given tissue or organ impacts its epigenetic clock.
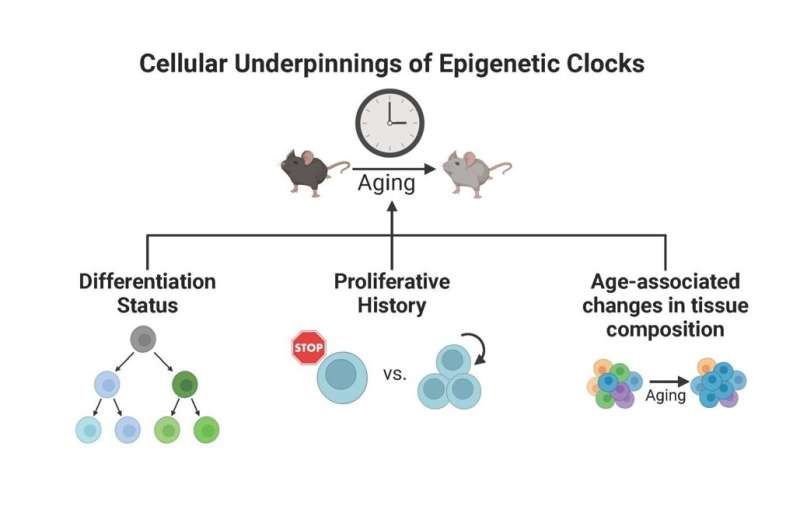
When measuring DNA changes in each single cell of a tissue individually, rather than in all cells mixed together, it became evident the stem cells in skeletal muscle, blood and trachea had a lower epigenetic age than the more mature cells.
A comparatively younger epigenetic age was not a universal feature of stem cells, though, as stem cells in other tissues such as skin and intestine had the same epigenetic age as the more mature cells.
Further experiments showed that the epigenetic age of a stem cell is linked to the rate at which it divides and makes new cells to regenerate and repair its tissue of origin. This rate was comparably higher in skin and intestine than in muscle or blood.
This research shows that the epigenetic age of a tissue as a whole is influenced by the frequency and activity of its stem cells, which in itself is subject to change in response to aging, injury, or disease. These findings have important repercussions for the interpretation of commercial biological age tests and will help to refine their fidelity and utility for the future.
More information: Dissecting the impact of differentiation stage, replicative history, and cell type composition on epigenetic clocks, Stem Cell Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.07.009. www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports … 2213-6711(24)00218-2