A third COVID vaccine dose improves defense for some clinically extremely vulnerable patients
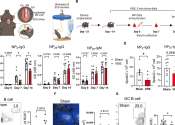
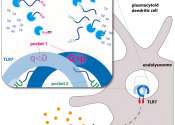
A major clinical trial has found that an additional COVID-19 vaccine dose led to the majority of clinically extremely vulnerable people mounting defensive antibodies against COVID-19.
14 hours ago
0
86