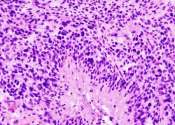
New imaging technique enables the study of 3-D printed brain tumors
Glioblastomas are complex, fast-growing malignant brain tumors that are made up of various types of cells. Even with aggressive treatment—which often includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy—glioblastomas are difficult ...
Mar 6, 2020
0
167