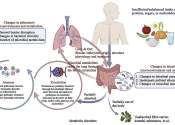
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of two commonly co-existing diseases of the lungs in which the airways become narrowed. This leads to a limitation of the flow of air to and from the lungs causing shortness of breath. In contrast to asthma, the limitation of airflow is poorly reversible and usually gets progressively worse over time.
COPD is caused by noxious particles or gas, most commonly from smoking, which trigger an abnormal inflammatory response in the lung. The inflammatory response in the larger airways is known as chronic bronchitis, which is diagnosed clinically when people regularly cough up sputum. In the alveoli, the inflammatory response causes destruction of the tissues of the lung, a process known as emphysema. The natural course of COPD is characterized by occasional sudden worsenings of symptoms called acute exacerbations, most of which are caused by infections or air pollution.
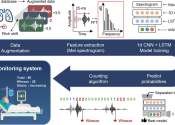
The diagnosis of COPD requires lung function tests. Important management strategies are smoking cessation, vaccinations, rehabilitation, and drug therapy (often using inhalers). Some patients go on to requiring long-term oxygen therapy or lung transplantation.
Worldwide, COPD ranked sixth as the cause of death in 1990. It is projected to be the third leading cause of death worldwide by 2020 due to an increase in smoking rates and demographic changes in many countries. COPD is the 4th leading cause of death in the U.S., and the economic burden of COPD in the U.S. in 2007 was $42.6 billion in health care costs and lost productivity.
COPD is also known as chronic obstructive lung disease (COLD), chronic obstructive airway disease (COAD), chronic airflow limitation (CAL) and chronic obstructive respiratory disease.