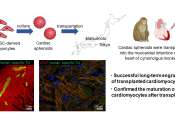
Using stem cell-derived heart muscle cells to advance heart regenerative therapy
Regenerative heart therapies involve transplanting cardiac muscle cells into damaged areas of the heart to recover lost function. However, the risk of arrhythmias following this procedure is reportedly high.
17 hours ago
0
62