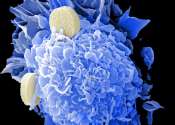
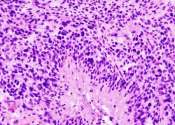
Chinese botanical medicine eases a cancer treatment side effect
An experimental drug based on ancient Chinese herbal medicine can help ease the toxic side effects of chemotherapy and radiation therapy in cancer patients, the results of a small new trial results suggest.
Aug 13, 2024
0
31