Study identifies new target in critical pain-regulating brain region
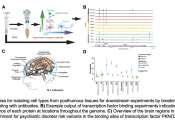
Chronic pain affects approximately 20% of the United States population and 30% of the global population. Along with sensory manifestations, chronic pain conditions also are associated with high rates of comorbid depression ...
Jul 11, 2024
0
1