Prognostic factors identified for intramedullary tibial nailing
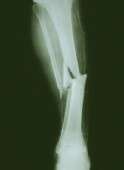
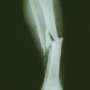
(HealthDay)—Fracture and surgical factors have been identified for the prediction of adverse outcomes after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures, according to a study published in the Oct. 3 issue of The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery.
Emil H. Schemitsch, M.D., from McMaster University in Hamilton, Canada and associates reviewed data from a multicenter trial of reamed and unreamed intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures in 1,226 patients. The correlation of baseline and surgical factors with negative outcomes was assessed.
The researchers found that the odds of negative events were significantly increased for patients with a high energy mechanism of injury (odds ratio [OR], 1.57); stainless steel versus titanium nail (OR, 1.52); a fracture gap (OR, 2.40); and full weight-bearing status after surgery (OR, 1.63). The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, late or early time to surgery, and smoking status did not correlate with increased risk. For patients treated with reamed nailing, open fractures had a higher risk of events (OR, 3.26), but this was not seem for patients treated with unreamed nailing. A decreased risk of events was seen for patients with open fractures who had wound management without any additional procedures (OR, 0.18) or with delayed primary closure (OR, 0.29), compared with patients who needed subsequent, more complex reconstruction.
"We identified several baseline fracture and surgical characteristics that may increase the risk of adverse events in patients with tibial shaft fractures," the authors write. "Surgeons should consider the predictors identified in our analysis to inform patients treated for tibial shaft fractures."
One or more of the authors disclosed financial ties to a third party in support of this work and/or an entity in the biomedical arena.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2012 HealthDay. All rights reserved.