iPads detect early signs of glaucoma in Nepal eye screening
Using a tablet screening app could prove to be an effective method to aid in the effort to reduce the incidence of avoidable blindness in populations at high-risk for glaucoma with limited access to health care, according to a study released today at AAO 2014, the 118th annual meeting of the American Academy of Ophthalmology. In this study, researchers from the University of Iowa, the University of Maryland, Johns Hopkins University, the University of Michigan and the Tilganga Eye Institute in Nepal used a free peripheral vision assessment app to screen approximately 200 patients in Nepal for glaucoma using an iPad. The results show promise for screening populations that have limited or no access to traditional eye care and certain ethnic groups that have a high risk of developing the disease.
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide, affecting more than 60.5 million people. The disease can be effectively treated; however, it generally does not present symptoms in its early stages, resulting in many patients being unaware that they suffer from the condition until it progresses to later stages. Early diagnosis can easily be achieved through a routine examination from an ophthalmologist – a medical doctor specializing in the diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment of eye diseases and conditions – or an optometrist. While it is relatively easy for patients with access to regular health care in developed nations to be screened for glaucoma during a routine eye examination, remote and underserved communities have limited or no access to such services, increasing their risk for glaucoma-related blindness.
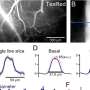
In order to determine if a screening test using mobile technology could be effectively administered to communities outside of a traditional clinical setting, the research team used the Visual Fields Easy app, which simulates a visual field test on an iPad (1st Generation), to screen more than 400 eyes for glaucoma.
Approximately half of the eyes screened were healthy "control" eyes and the other half were eyes with glaucoma. The researchers compared the screening results to those from the traditional industry standard visual field test, known as the Humphrey SITA Standard 24-2, and found that the two tests agreed between 51-79 percent of the time.
The best agreement was in patients with moderate and advanced visual field loss, while there was less agreement in patients with mild visual field loss. The researchers believe this was due to a high false positive rate for normal controls. While the agreement rate and cost-benefit ratio of the results were not strong enough to support using the method for screening general populations, the researchers believe that conducting screenings using a tablet can be an effective initial screening tool for high-risk groups, such as people of African or Hispanic ancestry, the elderly and people with limited or no access to traditional eye and health care. In addition, the screenings lasted an average of 3 minutes and 18 seconds – less than half the average time needed for the Humphrey SITA Standard test.
"Visual field testing equipment is neither portable nor affordable to some populations around the world, limiting entire regions from accessing health and eye care," said lead researcher Chris A. Johnson, Ph.D., director of the Visual Field Reading Center at the University of Iowa. "Although not perfect, the tablet glaucoma screening method could make a significant difference in remote locations where populations would not otherwise receive screening at all."