Novel inhibitory brain receptor may be mechanism for remission of epilepsy in adolescence
More than half of children with epilepsy outgrow their seizures, yet the mechanism underlying this remission is unknown.
Now, research led by SUNY Downstate Medical Center shows that, at the onset of puberty, the emergence of a novel inhibitory brain receptor, α4βδ (alpha four beta delta), reduces seizure-like activity in a mouse model of epilepsy.
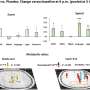
Sheryl Smith, PhD, professor of physiology and pharmacology at SUNY Downstate, explained, "Seizure-like discharges were three to four-fold greater before puberty and in pubertal mice that lack expression of this receptor. Administration of drugs that selectively enhance inhibition mediated by this receptor further decreased seizure-like activity in this model."
Dr. Smith concludes, "These findings suggest a mechanism for remission of epilepsy in adolescence and also suggest potential new therapies for childhood epilepsy."
The report, "Pubertal Expression of α4βδ GABAA Receptors Reduces Seizure-Like Discharges in CA1 Hippocampus," is published by Scientific Reports.
More information: Yang, L. et al. Pubertal Expression of α4βδ GABAA Receptors Reduces Seizure-Like Discharges in CA1 Hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 6, 31928; DOI: 10.1038/srep31928 (2016).