Dementia (taken from Latin, originally meaning "madness", from de- "without" + ment, the root of mens "mind") is a serious loss of global cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging. It may be static, the result of a unique global brain injury, or progressive, resulting in long-term decline due to damage or disease in the body. Although dementia is far more common in the geriatric population, it can occur before the age of 65, in which case it is termed "early onset dementia".
Dementia is not a single disease, but rather a non-specific illness syndrome (i.e., set of signs and symptoms) in which affected areas of cognition may be memory, attention, language, and problem solving. It is normally required to be present for at least 6 months to be diagnosed; cognitive dysfunction that has been seen only over shorter times, in particular less than weeks, must be termed delirium. In all types of general cognitive dysfunction, higher mental functions are affected first in the process.
Especially in the later stages of the condition, affected persons may be disoriented in time (not knowing what day of the week, day of the month, or even what year it is), in place (not knowing where they are), and in person (not knowing who they, or others around them, are). Dementia, though often treatable to some degree, is usually due to causes that are progressive and incurable.
Symptoms of dementia can be classified as either reversible or irreversible, depending upon the etiology of the disease. Less than 10% of cases of dementia are due to causes that may presently be reversed with treatment. Causes include many different specific disease processes, in the same way that symptoms of organ dysfunction such as shortness of breath, jaundice, or pain are attributable to many etiologies.
Without careful assessment of history, the short-term syndrome of delirium (often lasting days to weeks) can easily be confused with dementia, because they have all symptoms in common, save duration. Some mental illnesses, including depression and psychosis, may produce symptoms that must be differentiated from both delirium and dementia.
There are many specific types (causes) of dementia, often showing slightly different symptoms. However, the symptom overlap is such that it is impossible to diagnose the type of dementia by symptomatology alone, and in only a few cases are symptoms enough to give a high probability of some specific cause. Diagnosis is therefore aided by nuclear medicine brain scanning techniques. Certainty cannot be attained except with brain biopsy during life, or at necropsy in death.
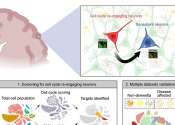
Some of the most common forms of dementia are: Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, frontotemporal dementia, semantic dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies. It is possible for a patient to exhibit two or more dementing processes at the same time, as none of the known types of dementia protects against the others.