Possible new pathway can overcome glioblastoma resistance
Glioblastoma, a lethal brain cancer, is one of the most resistant to available therapies and patients typically live approximately 15 months.
Previous research has focused on the activation of the apoptosis, or cell death, pathway using therapeutic agents such as tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL); however, the vast majority of these experiments have been stymied by resistance.
"Scientists in this field have been hoping to treat this cancer with this new type of apoptosis pathway-targeted therapeutic drug, and this new information may provide a path forward," said Chunhai "Charlie" Hao, M.D., Ph.D., a neuropathologist at Emory University.
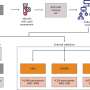
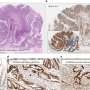
Using human glioblastoma samples and tumor-initiating cells or cancer stem cells, Hao and colleagues identified a possible new pathway for targeted therapies. Results of their work are published in Cancer Discovery, the newest journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
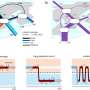
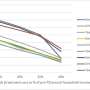
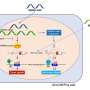
TRAIL treatment often leads to caspase-8-mediated apoptosis. However, study results showed that the A20 E3 ligase is highly expressed in glioblastomas and together with receptor interacting protein 1 (RIP1) and caspase-8, forms a signaling complex. Upon TRAIL interaction with this complex, the A20 E3 ligase triggers ubiquitination of RIP1, interferes with activation of caspase-8 and prevents caspase-8-initiated apoptosis.
"Previous research in this area has been unable to overcome the obstacle created by resistance. This research shows one of the mechanisms for how we can manipulate the ubiquitination process to overcome the resistance to the apoptosis-targeted cancer therapies," said Hao.
Understanding the mechanisms of resistance is vital to developing therapies going forward, according to Hao.