Study finds that tumor cells can prevent cancer spread
A new study finds that a group of little-explored cells in the tumor microenvironment likely serve as important gatekeepers against cancer progression and metastasis. Published in the January 17 issue of Cancer Cell, these findings suggest that anti-angiogenic therapies – which shrink cancer by cutting off tumors' blood supply – may inadvertently be making tumors more aggressive and likely to spread.
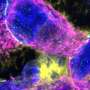
One approach to treating cancer targets angiogenesis, or blood vessel growth. In this new investigation, senior author Raghu Kalluri, MD, PhD, Chief of the Division of Matrix Biology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School (HMS), wanted to find out if targeting a specific cell type, the pericyte, could inhibit tumor growth in the same way that other antiangiogenic drugs do. Pericytes are an important part of tissue vasculature, covering blood vessels and supporting their growth.
Kalluri and his colleagues began by creating mice genetically engineered to support drug-induced depletion of pericytes in growing tumors. They then deleted pericytes in implanted mouse breast cancer tumors, decreasing pericyte numbers by 60 percent. Compared with wild-type controls, they saw a 30 percent decrease in tumor volumes over 25 days. However, contrary to conventional clinical wisdom, the investigators found that the number of secondary lung tumors in the engineered mice had increased threefold compared to the control mice, indicating that the tumors had metastasized.
"If you just looked at tumor growth, the results were good," says Kalluri. "But when you looked at the whole picture, inhibiting tumor vessels was not controlling cancer progression. The cancer was, in fact, spreading."
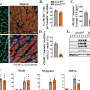
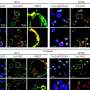
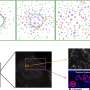
To understand the mechanism behind this increased metastasis, Kalluri and his team examined the tumor's microenvironment to find out what changes were taking place at the molecular level. They found a fivefold percentage increase in hypoxic areas in tumors lacking pericytes. "This suggested to us that without supportive pericytes, the vasculature inside the tumor was becoming weak and leaky—even more so than it already is inside most tumors—and this was reducing the flow of oxygen to the tumor," explains Kalluri.
"Cancer cells respond to hypoxia by launching genetic survival programs," he adds. To that end, the investigators found evidence of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a change that makes the cells more mobile, so they can travel through those leaky vessels to new locations, and makes them behave more like stem cells, so they are better able to survive. Experiments that demonstrated fivefold increases in protein markers of EMT showed that the cells had undergone the change. The team also found a fivefold increase in activation of Met, a receptor molecule that promotes cell migration and growth.
Importantly, the team found that these molecular changes occurred inside the smaller, pericyte-depleted tumors that had increased incidences of secondary tumors in the lungs in the mouse models. "This suggested that smaller tumors are shedding more cancer cells into the blood and causing more metastasis," says Kalluri. "We showed that a big tumor with good pericyte coverage is less metastatic than a smaller tumor of the same type with less pericyte coverage."
Because cancer therapies such as Imatinib, Sunitinib and others have been shown to decrease pericytes in tumors, the researchers' next step was to perform the same experiments in mice with primary tumors, only this time, using Imatinib and Sunitinib rather than genetic programs to decrease pericyte numbers. And while both Imatinib and Sunitinib caused a 70 percent pericyte depletion, the end results, stayed the same: metastasis increased threefold. "We showed that a big tumor with good pericyte coverage is less metastatic than a smaller tumor of the same type with less pericyte coverage," says Kalluri, who corroborated these findings in multiple types of cancer by repeating these same experiments with implanted renal cell carcinoma and melanoma tumors.
Additional experiments showed that combining pericyte-depleting drugs with the Met-inhibiting drug helped suppress EMT and metastasis.
Finally, to determine if the findings were relevant to patients, the scientists examined 130 breast cancer tumor samples of varying cancer stages and tumor sizes and compared pericyte levels with prognosis. They found that samples with low numbers of pericytes in tumor vasculature and high levels of Met expression correlated with the most deeply invasive cancers, distant metastasis and 5- and 10- year survival rates lower than 20 percent.
"These results are quite provocative and will influence clinical programs designed to target tumor angiogenesis," says Ronald A. DePinho, president of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. "These impressive studies will inform and refine potential therapeutic approaches for many cancers."
Meanwhile, for Kalluri, the work suggests that certain assumptions about cancer must be revisited. "We must go back and audit the tumor and find out which cells play a protective role versus which cells promote growth and aggression," says Kalluri. "Not everything is black and white. There are some cells inside a tumor that are actually good in certain contexts."