Research sheds light on important role of autophagy, or self-eating cells, in developing new anti-inflammatory therapies
Research just carried out in the Immunology Research Centre, led by Dr James Harris, based in the School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, shows that the process of autophagy regulates the production of inflammatory molecules and may therefore represent an effective target for the development of new anti-inflammatory therapeutics. The findings have been recently published online in the Journal of Immunology.
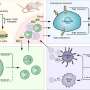
Inflammation is a key component of immune responses to infection, but when uncontrolled can lead to autoimmune diseases like Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, type I diabetes, ankylosing spondylitis, lupus, psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. In these diseases inflammation is mediated by molecules of the immune system called cytokines and cells that respond to these cytokines called T cells.
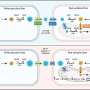
Autophagy is an ubiquitous process whereby cells degrade their own internal components, either to release valuable nutrients in times of starvation, or to remove damaged or noxious intracellular components. The work by Dr Harris and colleagues showed that autophagy also control release of the inflammatory cytokines and cells that have been implicated in the pathology of autoimmune diseases. The findings suggest that autophagy represents a potent target for new anti-inflammatory therapies, which could be beneficial in a range of autoimmune disorders.
The group, in combination with Professor Kingston Mills, now hopes to apply these findings to specific models of autoimmune disease. The work is funded by Science Foundation Ireland as part of a Strategic Research Cluster (SRC) award based in The Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute.
"Autophagy is a common cellular process that is important for the maintenance of normal cell functions. Our work has shown that this process is important in the control of inflammation and, as such, could represent a particularly efficacious target for new drugs against inflammatory conditions. There are over 80 different autoimmune diseases, most of which are chronic and debilitating and can be difficult and expensive to treat. Any research which helps us to better understand the underlying mechanisms behind the control of inflammation will ultimately lead to better treatments," explained Dr James Harris.
More information: Peral de Castro, C., Jones, S.A., Ni Cheallaigh, C., Hearnden, C.A., Williams, L., Winter, J., Lavelle, E.C., Mills, K.H.G. & Harris, J. (2012). Autophagy regulates IL-23 and innate T cells responses through effects on IL-1 secretion. Journal of Immunology 189(8), Oct . 15. www.jimmunol.org/content/189/8/4144.long