Receptors on bone cells connected to inflammatory bone loss and bone formation
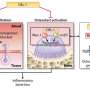
Inflammation-causing bacteria in contact with receptors on bone cells cause inflammation in patients, resulting in loosening of the teeth, loosening dental and orthopaedic implants or arthritis. The discovery indicates that the so-called Toll-like receptors also play an important role in the formation of new bone. This is according to a dissertation at Umeå University in Sweden.
The research builds upon previous discoveries of how various bacteria that cause inflammation communicate with the body's cells through Toll-like receptors that recognise the bacterial structure. Since the receptors can also be activated by internal substances in autoimmune diseases, the discovery can also be important in the understanding of how bone loss develops in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
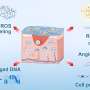
"We have discovered that Toll-like receptors on the surface of bone cells are activated by bacteria that are suspected to cause of loosening of the teeth or septic arthritis, which leads to the formation of osteoclasts –cells specialised in breaking down bone. If the mechanism controlling new bone formation via these receptors can be revealed it could be used to recreate bone lost due to inflammatory processes," says Ali Kassem, doctoral student at the Department of Molecular Periodontology at Umeå University.
The dissertation shows how the Toll-like receptors 2 and 5, which can stimulate bone loss, are also a part of the body's own mechanism for the formation of new bone tissue.
It is well known that bacteria can cause inflammation, but only in recent have researchers been able to show how bacteria communicate with cells in the body. The discovery of the gene called Toll (which is German for 'great') in the fruit fly and later, the function of this gene in humans were awarded the 1995 and 2011 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
More information: umu.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A861982&dswid=4525