Synapse discovery could lead to new treatments for Alzheimer's disease
A team of researchers led by UNSW Australia scientists has discovered how connections between brain cells are destroyed in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease - work that opens up a new avenue for research on possible treatments for the degenerative brain condition.
"One of the first signs of Alzheimer's disease is the loss of synapses - the structures that connect neurons in the brain," says study leader, Dr Vladimir Sytnyk, of the UNSW School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences.
"Synapses are required for all brain functions, and particularly for learning and forming memories. In Alzheimer's disease, this loss of synapses occurs very early on, when people still only have mild cognitive impairment, and long before the nerve cells themselves die.
"We have identified a new molecular mechanism which directly contributes to this synapse loss - a discovery we hope could eventually lead to earlier diagnosis of the disease and new treatments."
The team studied a protein in the brain called neural cell adhesion molecule 2, or NCAM2 - one of a family of molecules that physically connects the membranes of synapses and help stabilise these long lasting synaptic contacts between neurons.
The research is published in the journal Nature Communications.
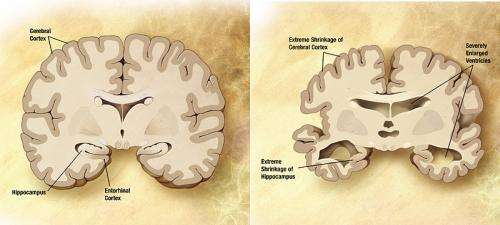
Using post-mortem brain tissue from people with and without the condition, they discovered that synaptic NCAM2 levels in the part of the brain known as the hippocampus were low in those with Alzheimer's disease.
They also showed in mice studies and in the laboratory that NCAM2 was broken down by another protein called beta-amyloid, which is the main component of the plaques that build up in the brains of people with the disease.
"Our research shows the loss of synapses is linked to the loss of NCAM2 as a result of the toxic effects of beta-amyloid," says Dr Sytnyk.
"It opens up a new avenue for research on possible treatments that can prevent the destruction of NCAM2 in the brain."
More information: Nature Communications, dx.doi.org/10.1038/NCOMMS9836