Higher risk of chronic kidney disease in 'healthy' obese
(HealthDay)—Overweight and obesity are associated with increased risk of development of chronic kidney disease (CKD), even in patients who are metabolically healthy, according to research published online Feb. 9 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Yoosoo Chang, M.D., Ph.D., of Sungkyunkwan University in Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study of 62,249 young and middle-aged, metabolically healthy, men and women who did not have CKD or proteinuria at baseline. The risk of incident CKD across categories of body mass index was assessed.
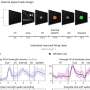
The researchers found 906 cases of incident CKD during 369,088 person-years of follow-up. Compared with normal-weight participants, the multivariable adjusted differences in five-year cumulative incidence of CKD, in cases per 1,000 persons, were −4.0 (95 percent confidence interval [CI], −7.8 to −0.3) in underweight, 3.5 (95 percent CI, 0.9 to 6.1) in overweight, and 6.7 (95 percent CI, 3.0 to 10.4) in obese participants, respectively.
"These findings show that metabolically healthy obesity is not a harmless condition and that the obese phenotype, regardless of metabolic abnormalities, can adversely affect renal function," the authors write.
More information: Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2016 HealthDay. All rights reserved.