Neurons anticipate body's response to food and water
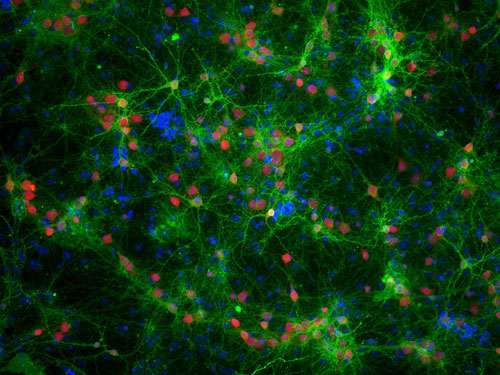
Using leading-edge technology, neuroscientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) gained new insight into the brain circuitry that regulates water and food intake. In a new study, the team of researchers monitored the activity of the neurons that secrete a hormone in response to ingesting food and water. In their paper, published online today in Neuron, the researchers demonstrated that a subset of neurons starts to prepare the body for an influx of water in the seconds before drinking begins. These neurons help regulate intake by anticipating the effects of drinking from the "top down," rather than taking cues from the body.
"This study supports the view that when we suddenly detect the availability of food or water, our body starts to prepare itself within seconds for the upcoming bout of eating or drinking," said co-corresponding author, Mark Andermann, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medicine in the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism at BIDMC. "We predict that deficits in this 'top-down' control could lead to overshoots in eating or drinking, with many negative consequences."
Andermann and colleagues, including co-corresponding author, Bradford B. Lowell, MD, PhD, a Professor of Medicine in the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism at BIDMC, recorded the activity of neurons responsible for releasing the anti-diuretic hormone vasopressin in mice. Vasopressin plays a crucial role regulating the body's relative concentration of water versus salt after eating or drinking, which could otherwise dramatically alter the mix.
"It's critical to survival that the body has ways to prevent the water concentration outside of cells from changing," said Lowell. "Anticipating the future consequences of ingesting water helps the body get a head-start on managing water balance. The form of rapid, top-down control of this process that we discovered is one important way of managing it."
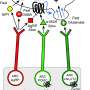
In their experiments, Andermann and Lowell watched as the activity of vasopressin-releasing neuron rapidly decreased - within seconds - when water was presented to water-restricted rodents, before they even drank it. In contrast, the sight and smell of food increased the activity in these neurons - again, within seconds - but only following food consumption. That difference in timing suggested that separate neural networks regulate these reactions to water and to food.
"This type of rapid regulation was not known to exist and has only been discovered in the last year for hunger neurons and for vasopressin neurons," said Lowell. "It likely occurs for all forms of homeostatic control. It's interesting to speculate whether there are individuals out there who have abnormalities in this kind of top-down control."
"By the same token, we may one day learn that enhancing this top-down control might be a way of regulating meal size without interfering with baseline appetite or with the pleasure of taking the first bite of something delicious," Andermann said, adding their high-tech methodology will allow them to further investigate the neurons directly "upstream" of the vasopressin neurons. "Because we can now monitor and manipulate the activity of specific sets of neurons, we're getting closer to being able to directly test these hypotheses and working toward strategies to improve human health."