Scientists make autism advance using monkey model

Autism is a common neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired social communication and restricted and repetitive behavior or interests. The reported prevalence of autism has been rising worldwide. Due to the application of large-scale exome sequencing in recent years, hundreds of novel autism-associated genes have been identified.
Mutations in SHANK3 remain one of the best characterized and replicated genetic defects associated with autism in humans. Genetically modified Shank3 mutant mice have served as valuable tools to dissect the pathophysiology of SHANK3 as related to autism. However, the significant evolutionary differences between the mouse and human brain and associated behaviors pose many challenges to assessing the translational value of mouse models in relation to humans, and highlight the need to develop non-human primate models.
Recently, researchers from Dr. ZHANG Yongqing's group at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found neurodevelopmental abnormality in a SHANK3-deficient non-human primate for the first time.
Using CRISPR/Cas9 to target the SHANK3 gene in the embryos of cynomolgus monkeys, the researchers successfully generated three mutant monkey offspring with various deleterious mutations in the SHANK3 gene. They analyzed the targeted mutations in various tissues from the three animals and brain regions of the deceased animals by immunochemical analysis.
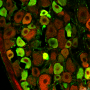
Complete SHANK3 deficiency resulted in a significant reduction in postsynaptic proteins such as GluN2B, PSD95, mGluR5 and increased cytosolic localization of Homer1b/c. The number of mature neurons was markedly reduced but activated astrocytes were increased in the prefrontal cortex in the SHANK3-deficient brain. The neuropathology caused by the complete loss of SHANK3 in the monkey brain is remarkably distinct from findings reported from Shank3 knockout mice.
These findings indicate that SHANK3 is essential for the early development of primate brains. Understanding the novel role of SHANK3 in early brain development is critical to the autism field. The research, titled "Altered neurogenesis and disrupted expression of synaptic proteins in prefrontal cortex of SHANK3-deficient non-human primate," has been published in advance online in Cell Research.
More information: Hui Zhao et al, Altered neurogenesis and disrupted expression of synaptic proteins in prefrontal cortex of SHANK3-deficient non-human primate, Cell Research (2017). DOI: 10.1038/cr.2017.95