Soft furniture doesn't cushion risk of falls by young children
Most parents know how easily young children can fall down stairs or tumble off tables at home. Soft, padded furniture like beds and sofas may seem like less of an injury threat. But a new research abstract being presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2018 National Conference & Exhibition shows more than 2 million children under age 5 were treated in hospital emergency departments for soft furniture-related injuries between 2007 and 2016.
The study abstract, "Bed and Sofa-Related Injuries to Young Children Treated in US Emergency Departments, 2007-2016," will be presented on Monday, Nov. 5, at the Orange County Convention Center in Orlando, Fla.
"Parents often leave young children on a bed or sofa, stepping away for a bit and thinking it's not dangerous," said lead researcher and author Viachaslau Bradko, MD. "But our research shows that these types of falls are now the most common source of injury in this age group," he said. In fact, he said, children were 2.5 times more likely to be hurt by falls from beds and sofas than they were from stair-related injuries.
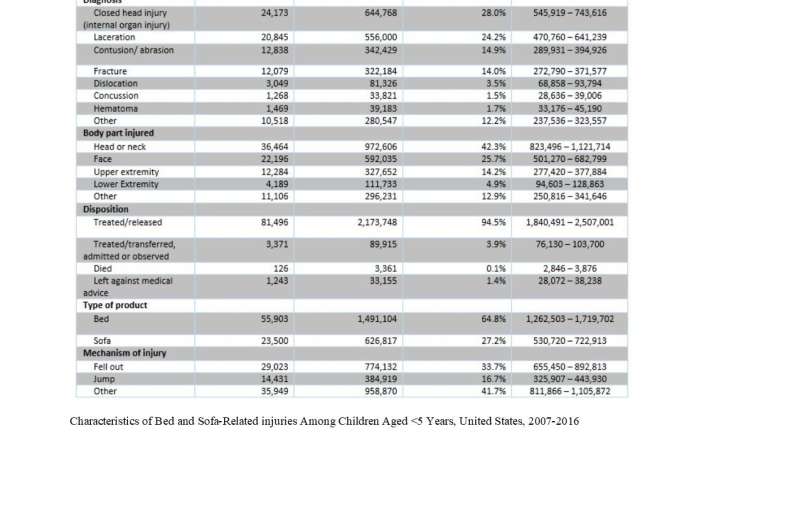
For the study, the first to use a nationally representative sample to study bed and sofa-related injuries, researchers analyzed the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission National Electronic Injury Surveillance System data from 2007 through 2016. They found that an estimated 2.3 million children age 5 and younger were treated for soft furniture-related injuries during that time period, averaging 230,026 injuries per year.
Among other findings:
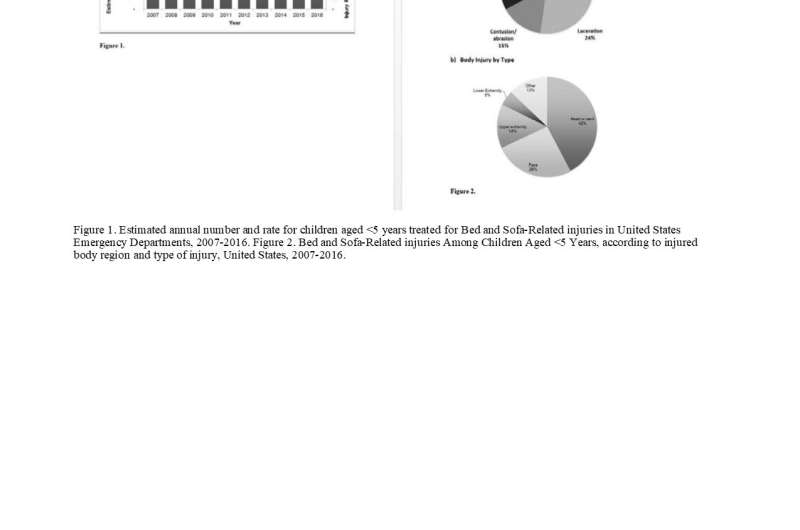
- Approximately 62 percent of children had injuries to the head and facial region. Fortunately, severe, life-threatening trauma was rare, but 2.7 percent of patients were hospitalized.
- Children younger than a year old when they were injured accounted for 28 percent of injuries among the patients, and they were more than twice as likely to be hospitalized than children over age 1.
- Boys (56 percent of cases) were more likely to be injured than girls.
In addition, bed and sofa-related injuries among children under age 5 increased by more than 16 percent during the study period, said Dr. Bradko, a Post-Doctoral Clinical Research Fellow in the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery at Texas Children's Hospital.
"With falls from beds and sofas hurting such a large and growing number of infants, toddlers and young children, there's a serious need to step up prevention efforts," he said. This includes reminding parents to constantly keep their eyes on young children when they're on elevated surfaces, including soft furniture, for example. In addition, he said, the findings should prompt manufacturers to improve safety design and consider warning labels. For example, furniture manufacturers might advise consumers against allowing young children to be left unattended on beds without properly installed guard rails or allowing children to jump on or off furniture above a certain height.


















