Risk factors for falling are different in older men versus older women
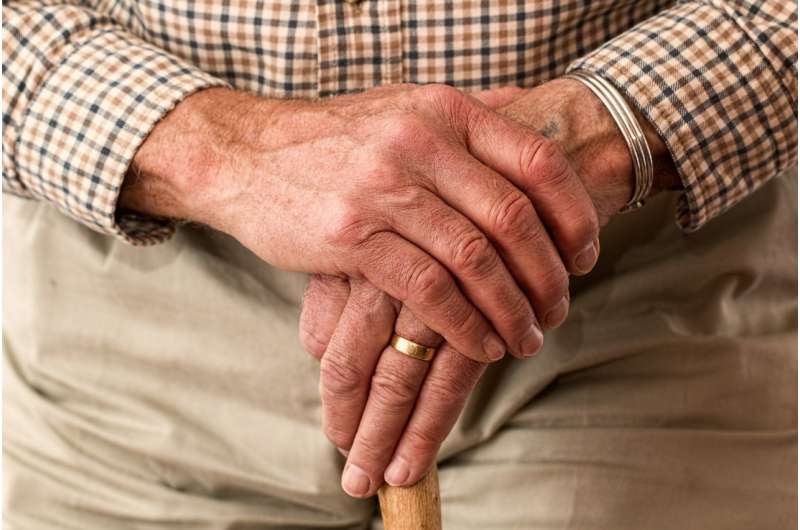

Different factors were associated with falling in men versus women in a study of 3,112 community-dwelling adults aged 60 years and older. The findings are published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
In the short term, living alone, needing help with activities of daily living, and previous falls were independently associated with injurious falls in women. Low systolic blood pressure, impaired ability to rise from a chair, and previous falls were associated with injurious falls in men.
Long-term risk factors were underweight, cognitive impairment, use of medications associated with an increased risk of falling, and needing help with activities of daily living for women and smoking, heart disease, impaired balance, and a previous fall for men.
"Despite the numerous studies on risk factors for falls in older adults, studies examining sex differences are scarce," said lead author Stina Ek, of the Karolinska Institutet, in Sweden. "The results of our study suggest that men and women have different fall risk profiles. If we take these sex differences into consideration in screening and prevention programs for falls, we may potentially enable a better person-centered approach."
More information: Stina Ek et al, Risk Factors for Injurious Falls in Older Adults: The Role of Sex and Length of Follow-Up, Journal of the American Geriatrics Society (2018). DOI: 10.1111/jgs.15657