Early EEG helps predict cardiac arrest outcomes in comatose

(HealthDay)—Early electroencephalography (EEG) reliably predicts the outcome of comatose patients after cardiac arrest, according to a study recently published in the Annals of Neurology.
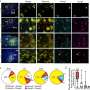
Barry J. Ruijter, M.D., Ph.D., from the University of Twente in Enschede, Netherlands, and colleagues assessed whether early EEG can reliably predict outcomes among comatose patients after cardiac arrest. Blinded reviewers assessed five-minute EEG epochs at eight predefined time points from six hours to five days after cardiac arrest.
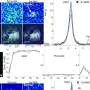
The researchers found good outcomes for 46 percent of 850 patients. At six or more hours after cardiac arrest, generalized suppression and synchronous patterns with ≥50 percent suppression predicted poor outcome without false positives. At 12 and 24 hours after cardiac arrest, the summed sensitivity was 0.47 (95 percent confidence interval [CI], 0.42 to 0.51) and 0.30 (95 percent CI, 0.26 to 0.33), respectively, with a specificity of 1.00 at both time points (95 percent CI, 0.99 to 1.00). At ≥36 hours, sensitivity for poor outcome was ≤0.22. In contrast, continuous EEG patterns at 12 hours predicted good outcome, with a sensitivity of 0.50 (95 percent CI, 0.46 to 0.55) and specificity of 0.91 (95 percent CI, 0.88 to 0.93), while specificity for the prediction of good outcome at 24 hours or later was <0.90.
"EEG allows for reliable prediction of poor outcome after cardiac arrest, with maximum sensitivity in the first 24 hours," the authors write.
One author is cofounder of a company that supplies EEG systems used to collect study data.
More information: Abstract/Full Text
Copyright © 2019 HealthDay. All rights reserved.