Disruption of glycine receptors to study embryonic development and brain function
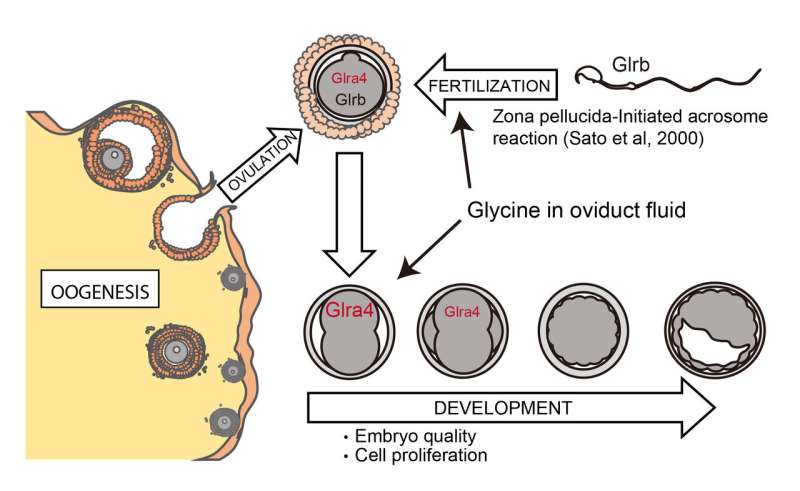
Glycine receptors are among the most widely distributed inhibitory receptors in the central nervous system and have important roles in a variety of physiological processes. Researchers from Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience (MPFI), University of Toyama, Yamagata University, Cairo University, RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences and Setsunan University collaborated to study glycine receptors, particularly glycine receptor alpha-4 (Glra4), during development. In a recent publication in the journal Reproduction, they demonstrated that Glra4 is not a brain-exclusive gene, as was believed, but actually facilitates early embryonic development in mice.
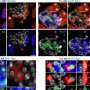
Hirofumi Nishizono, research associate of Yasuda Lab and first author of this publication, explained that in order to fully understand the function of a specific gene, it is necessary to study a condition in which this gene is deleted. By applying in vitro fertilization in combination with CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to mouse embryos, the team generated a genetically modified mouse in which the Glra4 gene has been disrupted.
One of the remarkable results shows that Glra4 plays a critical role in the early development of fertilized eggs, facilitating the development of the blastocyst, a structure formed in the early development of mammals, maintaining embryo quality and litter size in mice. Interestingly, they have also shown that different types of glycine receptors are expressed not only in mouse fertilized eggs but also in fertilized eggs of humans and bovine, suggesting that the role of these receptors in early embryonic development is conserved across species. Moreover, while Glra4 is a pseudogene in humans, they use a different type of glycine receptors (GLRA2), which are active in humans, for this process.
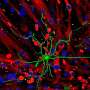
Nishizono is currently investigating the effects of the disruption of glycine receptors in the brain. He is conducting behavioral tests to evaluate if the deletion of Glra4 affects brain function of mice. Some preliminary data indicate that the deletion of Glra4 is associated with phenotypes related to psychiatric disorders. Yasuda Lab will continue to produce genetically modified mice to investigate the role of different molecules involved in learning and memory as well as various brain disorders.
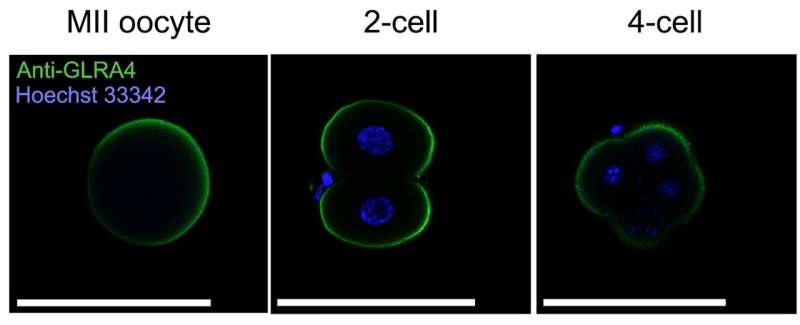
More information: Hirofumi Nishizono et al, Glycine receptor α4 subunit facilitates the early embryonic development in mice, Reproduction (2019). DOI: 10.1530/REP-19-0312