Study explores how older people manage distress
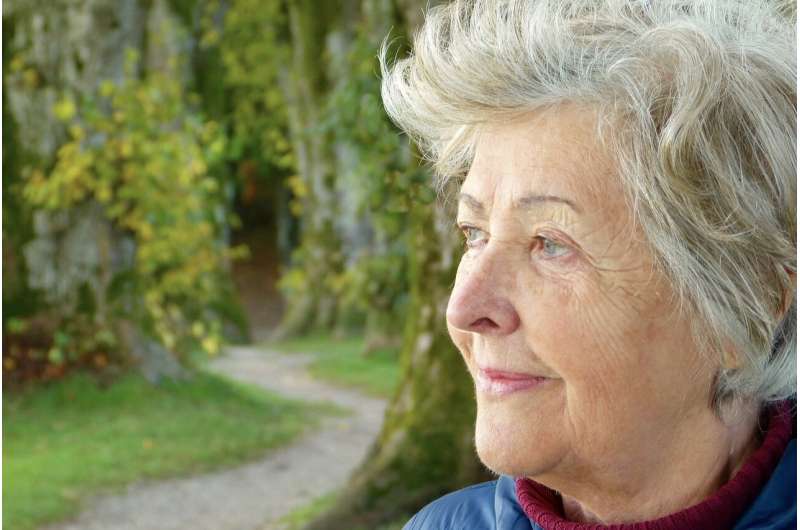

A team of researchers from Keele University has found that it is uncommon for older adults to consult their GP during times of distress due to a lack of acceptable treatments.
Distress is not diagnostically labelled as a mental health problem but is an expected emotional response to a negative life event. Experiences which are common in later life may trigger such a response.
The research, published in BMC Family Practice, determines the coping mechanisms employed by older adults that self-identify as distressed and aims to clarify the role that primary care plays in supporting individuals who decide to consult healthcare services.
Dr. Alice Moult from Keele's School of Medicine, and Dr. Tom Kingstone and Professor Carolyn Chew-Graham from the School of Primary, Community and Social Care, interviewed older adults who self-identified as distressed and found that various forms of loss contributed to their distress for example bereavement or loss of physical mobility.
Older adults are active in wanting to improve their mood, as some participants described their own self-management strategies including pursuing independent activities, seeking social support, attending community groups and attending church. It is, however, less common for older adults to consult a GP when distressed, with only a few participants seeking this option due to a lack of acceptable treatments offered as they did not want to take medication or engage in 'talking therapies'. It was found that a persistence of mood problems could be a major reason for older adults to eventually seek help from a GP.
To help alleviate feelings of distress, the research suggests that GPs could discuss the causes behind why patients are suffering and provide information about a range of management options including how the individual may self-manage their mood, the use of social prescription by sign-posting older people to local third sector services, and the potential use of medication or talking therapies.
Dr. Moult said, "We hope that this piece of research will increase awareness amongst healthcare professionals of the role they play in supporting distressed older adults. It is hoped that the findings may also provide valuable insight to why self-management strategies can prove unsuccessful and inform the development of alternative solutions."
More information: Alice Moult et al. How do older adults understand and manage distress? A qualitative study, BMC Family Practice (2020). DOI: 10.1186/s12875-020-01152-7