Here's what to know about flu shots this year
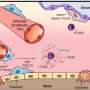
Bad as it has been these past few months to live with the danger of coronavirus, things are about to get worse. Fall is approaching and with it comes that other respiratory virus that puts thousands of Americans in the hospital every year: influenza.
Prepare for an onslaught of public service messages begging you to get a shot not only to protect yourself and your vulnerable loved ones but an entire health system already strained by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Hospitals often fill up in December and January when flu season really takes off, said Susan Bailey, an allergy and immunology specialist in Fort Worth who is president of the American Medical Association. "If hospitals are already full of coronavirus patients, where are the influenza patients going to go?" she asked. The AMA encourages flu vaccines every year, but will have a larger campaign with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Ad Council this year.
To further complicate matters, the symptoms of flu and COVID-19 can be so similar that doctors won't be able to tell them apart without testing. A new test that can detect influenza A, influenza B and COVID-19 has received emergency authorization from the FDA, but is not yet available. That means patients could need two tests to get a diagnosis
Doctors need to know which one they're dealing with because there are anti-viral medications for flu. More importantly, people with coronavirus need to be isolated.
And, doctors know that patients can get the coronavirus and flu at the same time. They do not know yet whether that results in worse illness than either would cause alone, but it stands to reason that it might. Flu and the coronavirus tend to be most dangerous for the same groups: the elderly and those with chronic health problems. There isn't a vaccine for coronavirus yet, they said, but you can do something about the flu.
"We want to make sure we take flu off the table," said L.J. Tan, chief strategy officer for the Immunization Action Committee, a nonprofit that promotes vaccination.
But worries about coronavirus could make vaccination more challenging, said William Schaffner, medical director for the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases (NFID) and professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. Telemedicine can't deliver vaccines, he said, and rates for other types of vaccination have dropped.
"We're very concerned about that," he said. "There's a need to get (the flu shot), but there are barriers to actually getting it done."
The foundation is also stepping up vaccine promotion efforts, especially for people with chronic illness.
On the other hand, demand could be unusually high for what may feel like a rare and much-needed act of control.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, drug manufacturers say they will produce 194 to 198 million doses of vaccine this season, up from 175 million last year. Pennsylvania's health department is getting 860,000, more than twice the usual number of doses, said Rachel Levine, the state's secretary of health. New Jersey will also have more.
Many of the government vaccines will go to county health departments, people on Medicaid and users of federal health centers. Amber Tirmal, immunization program manager for the Philadelphia Department of Health, said this year the health department can give shots to people regardless of their insurance status. "The CDC is doing that because they recognize how important flu vaccine is this year," she said. The city's immunization campaign likely will start in October, she said.
While some doctors offices have not yet received flu vaccines, some pharmacies have already put out the signs saying it's time to get one.
With all that in mind, here are answers to some questions you may have.
When should I get my shot?
Ideally, doctors said, it's best to wait until September or well into October. Schaffner suggests mid-September to mid-November. The effectiveness of the shot wanes over time. In most people, it stays strong for six months or so, but people over 65 tend to lose immunity more quickly. Waiting a little longer to get the shot improves the odds that you'll be protected until the end of the season, which is usually around March or April. However, it takes two weeks to get the shot's full benefit, so you want to get it before cases become more common in the fall. That's often sometime in November. If you haven't already gotten sick, you can get shots into the spring.
But if it's convenient to get it sooner, especially if you're young and healthy, take it. "The best time to get the flu vaccine is any time," said Levine, whose agency will start its push around Labor Day.
Will the flu shot protect against COVID-19?
No.
Will this be a bad flu season?
This is unpredictable. Scientists look to countries in the Southern Hemisphere to see which strains of flu are likely to circulate here. However, Thomas Fekete, an infectious diseases specialist at Temple University Hospital, said they are not always good for predicting how many cases the U.S. will have because their populations are so different. So far, Australia, which Tan said increased flu vaccination rates this year, seems to be having a mild season. Schaffner said Chile and Brazil, countries the U.S. typically watches to predict flu, are so "awash" in coronavirus that they lack the resources to track flu.
Measures to prevent COVID-19—mask wearing, hand washing, distancing—should reduce spread of flu as well, though compliance in this country is spotty.
Schaffner said Australia and New Zealand have made social distancing, testing and contact tracing high priorities. "We haven't made that commitment in the U.S.," he said.
The shot is an easy way to add protection. "This year, we will still see people die as a result of influenza and we want to prevent as many of those deaths as possible," said Joseph Teel, a family medicine doctor who is vice chair for clinical operations at Penn Medicine.
Which kind of flu shot should I get?
Some types protect against three strains of virus (trivalent) and some against four (quadrivalent). Doctors said you should go for quadrivalent if you have a choice. It's recommended that people over 65 get a high-dose version of the shot that works better in older people.
But don't hold out if a particular option isn't available. "I think the best vaccine for someone," the AMA's Bailey said, "is the one that they're easily able to obtain."
Who should get a flu shot?
The shot is recommended for almost everyone over the age of six months. Fekete said kids should definitely get the shots because they are big flu spreaders. Usually, fewer than half of people eligible for flu shots actually get them, Tan said.
Where should I get the shot this year?
As many as a fifth of people are used to getting their vaccine through their employers, Tan said. If they're working from home now, they may have to look for alternatives, like pharmacies, urgent care centers, doctors offices and vaccination drives.
Bailey suggests calling your doctor to see if he or she will have shots. Schaffner said some doctors will be scheduling flu shot appointments either early or late in the work day, so they can be done quickly and efficiently. Some may even be done outside for additional coronavirus protection, since the virus is less likely to spread outdoors.
A CVS spokesman said the chain will begin making appointments for vaccines next month to make it easier for customers to get in and out fast. Teel said Penn's practices are currently planning alternative locations to improve efficiency.
Tan said he has heard of plans to do drive-up vaccinations where people can just stick an arm out a window. Another possibility is outside shots for walkers or even vaccination stations under tents.
How is the government going to keep track of flu this year?
In the past, the government's surveillance system has relied on tracking people with flu-like symptoms in some settings. It also tracked hospitalizations and deaths connected with flu-like symptoms and pneumonia. Now it has two viruses that causes similar symptoms and pneumonia.
"It's going to be a challenge," Levine conceded.
The prospect of a double-barreled flu/coronavirus seasons likely means there will be a lot more testing for both viruses. "You can't just say that someone has influenza-like symptoms," Levine said.
©2020 The Philadelphia Inquirer
Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.