Molecular mechanism of cross-species transmission of primate lentiviruses
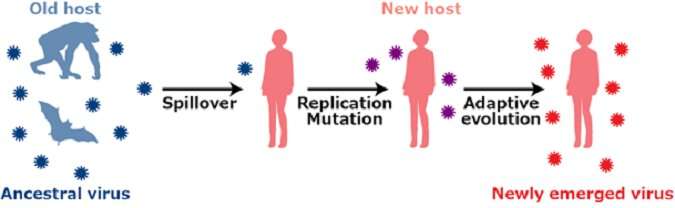
Humans are exposed continuously to the menace of viral diseases such as those caused by the Ebola virus, Zika virus and coronaviruses. Such emerging/re-emerging viral outbreaks can be triggered by cross-species viral transmission from wild animals to humans.
To achieve cross-species transmission, new hosts have to be exposed to the virus from the old host. Next, the viruses acquire certain mutations that can be beneficial for replicating in the new hosts. Finally, through sustained transmission in the new host, the viruses adapt further evolving as a new virus in the new host. However, at the outset of this process, the viruses have to overcome "the species barriers," which hamper viral cross-species transmission. Mammals including humans have 'intrinsic immunity' mechanisms that have diverged enough in evolution to erect species barriers to viral transmission.
HIV-1 most likely originated from related precursors found in chimpanzees and gorillas
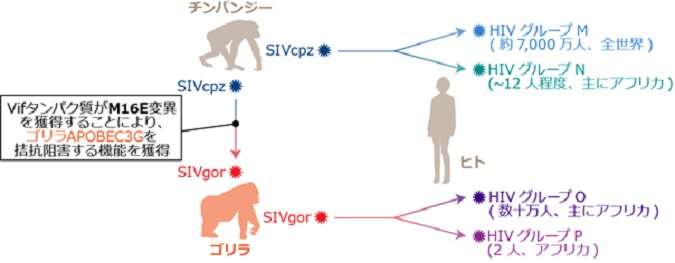
HIV-1, the causative agent of AIDS, most likely originated from related precursors found in chimpanzees (SIVcpz) and gorillas (SIVgor), approximately 100 years ago.
Additionally, SIVgor most likely emerged through the cross-species jump of SIVcpz from chimpanzees to gorillas.
However, it remains unclear how primate lentiviruses successfully transmitted among different species. To limit cross-species lentiviral transmission, cellular "intrinsic immunity," including APOBEC3 proteins potentially inhibit lentiviral replication. In contrast, primate lentiviruses in this evolutionary "arms race" have acquired their own "weapon," viral infectivity factor (Vif), to antagonize the antiviral effect of restriction factors.
A great ape APOBEC3 protein can potentially restrict the cross-species transmission of great ape lentiviruses
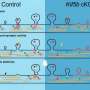
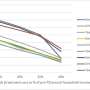
A research group at The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo (IMSUT) showed that gorilla APOBEC3G potentially plays a role in inhibiting SIVcpz replication. Intriguingly, the research group demonstrated that an amino acid substitution in SIVcpz Vif, M16E, is sufficient to overcome gorilla APOBEC3G-mediated restriction.
"To our knowledge, this is the first report suggesting that a great ape APOBEC3 protein can potentially restrict the cross-species transmission of great ape lentiviruses and how lentiviruses overcame this species barrier. Moreover, this is the first investigation elucidating the molecular mechanism by which great ape lentiviruses achieve cross-species transmission," said the lead scientist, Kei Sato, Associate Professor (Principal Investigator) in the Division of Systems Virology, Department of Infectious Disease Control, IMSUT.
More information: Yusuke Nakano et al. A role for gorilla APOBEC3G in shaping lentivirus evolution including transmission to humans, PLOS Pathogens (2020). DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008812